Categories
 Department of Anthropology
Department of Anthropology
 |
Dr Theint Ei Ei Khaing Head of Department- Anthropology Professor Ph.D. (Anthropology) Department of Anthropology, Yadanabon University, Mandalay, Myanmar (+95-095030754) matheint762010@gmail.com |
Staff
| Professor | – | 1 |
| Associate Professor | – | 2 |
| Lecture | – | 3 |
| Assistant Lecturer | – | – |
| Tutor | – | 2 |
| Total | – | 8 |
History of the Department
- Established in the year 2000 by the Rector U Win Maung and Pro-rector U Than Nwe.
- First appointed Head Department – Dr Aye Aye Aung (Professor).
- Department of Anthropology offers BA, BA(Hons), MA.
Vision
- To set up acceptable forms and functions of human diversity and multi culture at the present in the past through intensive field work
- To increase students’ knowledge and skills in the intellectual, social and economic development related to the local and global levels
- To develop the creative research, teaching and leading voice for the practice of public, collaborative and community engaged Anthropology
Mission
- To study the holistic bio-cultural diversity in the present and the past
- To support the students to become skillful in research and theories, writing and application of Anthropological knowledge to enhance academic excellence and professional development
- To offer the highest quality instruction in the discipline of Anthropology through implementing their community development
Programs Offered
| BA. / BA.(Hons) in Anthropology |
| MA. in Anthropology |
Curriculum
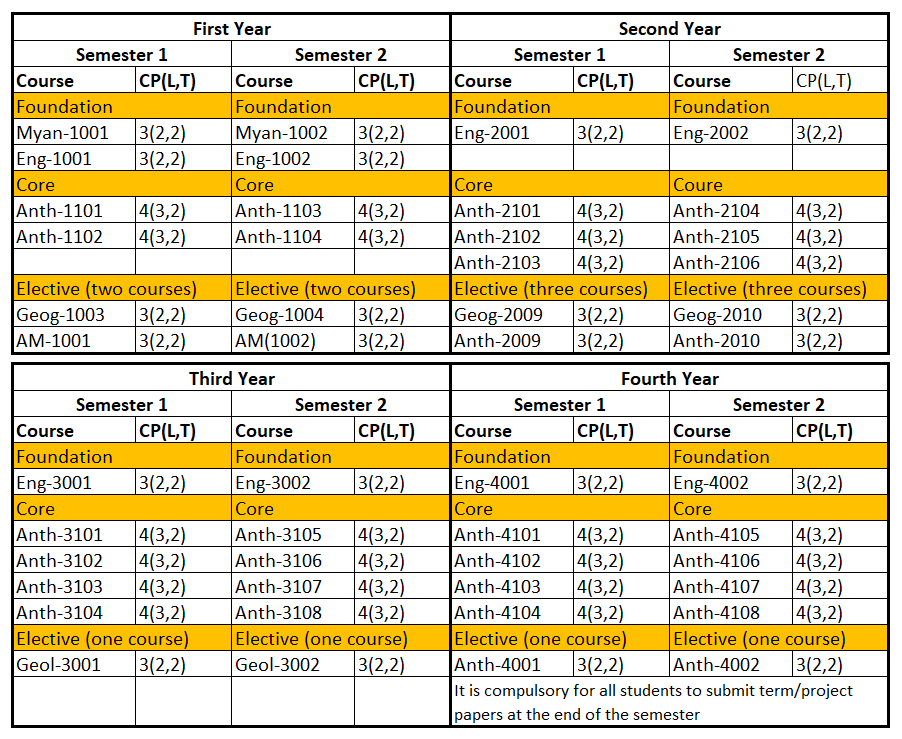
BA in Anthropology
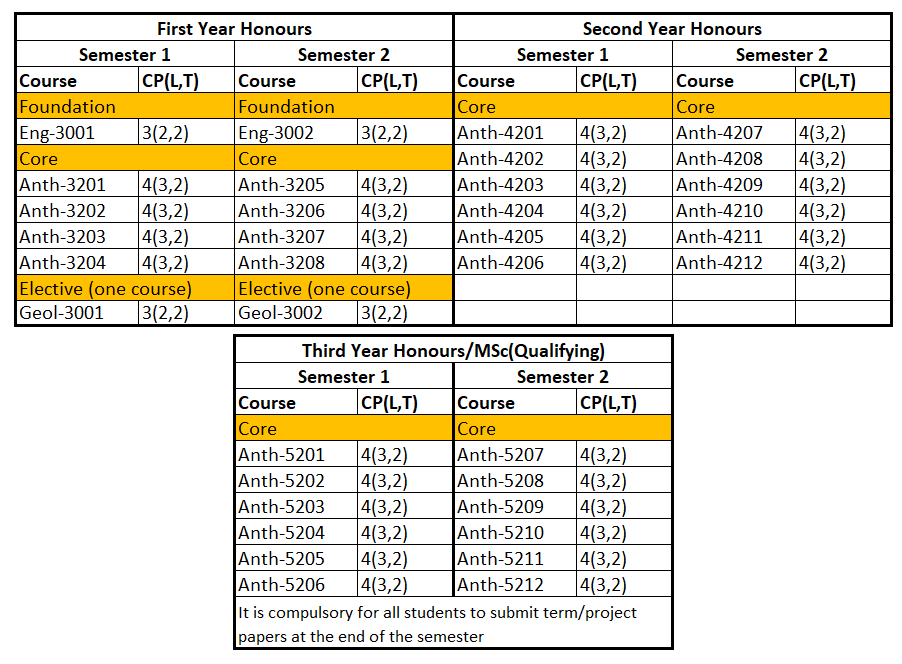
BA (Honours)
Students who passed second year with GPA greater than 4 are eligible to attend BA. (Honours) classes for three more years. After finished successfully, they are earned BA. (Hons) degree majoring in Anthropology. And then, students who earned BA. (Hons) with GPA greater than 4 are eligible to attend Master degree.
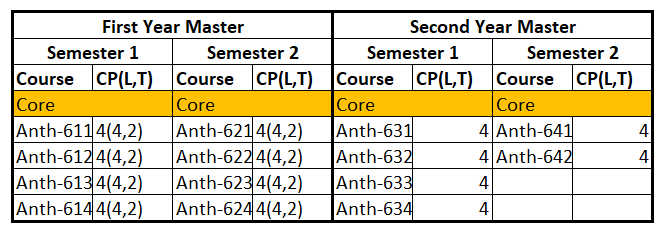
MA in Anthropology
After finished first year Master, they do research in second year Master. And then they are earned MA degree in Anthropology.
Descriptions Modules Offered
- The definition of Anthropology
- Historical Background of Anthropology
- The nature and scope of Anthropology
- Social Anthropology
- The relation of Anthropology to other disciplines
- Anthropological study of the simple/ primitive societies
- The study of mankind as a whole
- The application of Anthropology
- Introduction to Cultural Anthropology
- Defining the features of culture
- Cultural history of the old world
- The main level of cultural growth
- Evolution of culture
- Anthropological usages of the term culture
- Man and culture
- The relation of culture to society
- The unity and diversity in culture
- Ethnic groups of Myanmar
- Anthropology Today
- What Anthropologists do?
- Anthropology as social science
- Ethical code of Anthropologists
- The holistic approach of Anthropology
- Difficulties of Scientific approach
- Components of culture
- Defining features of culture
- Some assumptions about culture
- Culture and subcultures
- The relation of habit to culture
- The relation of habitat and technology to material culture
- The evolution cultural behavior
- The relation of personality to culture
- Ethnic groups of Myanmar
- Physical Anthropology or Biological Anthropology
- Sub-field of Physical Anthropology
- Method of measurements in Physical Anthropology
- Darwin’s theory of evolution
- The origin of species
- Natural selection
- Mendel’s experiment
- The classification of man
- Methods of classification
-homologous and Analogous traits
-Primitive and derived traits
- The vertebrates and their characteristics
- The mammals
- Mammalian evolution and primate origins
- The definition of fossilization and the principles of paleontology
- Primate paleontology
(a) Pliopithecus
(b) Proconsul
(c) Dryopithecus
(d) Oreopithecus
(e) Ramapithecus
(f) Amphipithecus
- The definition of Archaeological Anthropology
- The scope and aim of Archaeological anthropology
- Ways of Findings
- Excavation Methods
- Methods of Dating
- Prehistoric Sites in Myanmar
- Proto-historic Sites in Myanmar
- Historic Sites in Myanmar
- The definition of Applied Anthropology
- The Ethic and Responsibilities of the Applied Anthropology
- Applied Anthropology and the Subdisciplines
- Ethnography in Applied Anthropology
- The Roles of Applied Anthropologists in Planned Change
- Medical Anthropology
- Ethnocentrism, Cultural Relativism, and Human Rights
- Fieldwork and Its Uses
- Difficulties of Instituting Planned Change
- -Target Population
- Discovering and Utilizing Local Channels of Influence
- Primate origins
- -Continental drift and primate evolution
- Primates traits
- Types of primates
- Trends in hominid evolution
- -Bipedalism
- -Expansion of the brain
- -Reduction of the Face, Teeth and Jaw
- The first Hominid
- The emergence of modern human
- Theories about the origins of modern human
- Human palaeontology
(a) Australopithecine
(b) Homo habilis
(c) Homo erectus
(d) Heidelberg Man
(e) Cro-Magnon Man
(f) Neanderthalensis
(g) Rhodesian Man
(h) Homo sapiens
(i) Homo sapiens sapiens
- The History of Archaeological Anthropology
- The Nature of Archaeological Evidence and its limitation
- The Classification of Archaeological Materials
- Prehistoric Sites in Myanmar
- Proto-historic Sites in Myanmar
- Historic Sites in Myanmar
- The role of Applied Anthropologists
- Applied Anthropology in the study of Ethnography
- The problem of the Ethnocentrism
- Stone tools for modern surgeons
- Dealing with infant mortality
- Applied Anthropology in agricultural development
- Protecting cultural heritage
- Anthropology and the world of business
- Discovery and utilizing local channels of influence
- Applied Anthropology and culture change
- The meaning of Social Organization
- Basic Social Groups: Sex, Age grade, Class and Caste, Occupation, Locality
- Marriage
- Preferential Mating
- Extra Marital Relation
- Rules and Restriction of Marriage
- Ways of Acquiring a Wife
- Divorce
- Definition of Religion
- Anthropological approach to religion
- Origins of belief and variation in religious systems
- Religious Practitioners
- Magic and Religion
- Organization of Religion
- Anthropological use of the term “Culture”
- Anthropological use of the term “Personality” and “Character”
- Culture and Individual
- Basic personality
- Modal personality
- Group personality
- Normal personality and abnormal personality
- National Character
- Dependence Training
- The Development of personality
- Factors Producing Human Variation
- Biological Variation in Human Population
- Racial Approach to Variation
- Forms of Family
- Residence Patterns of Extended Family
- Kinship and Descent
- Patrilineal Organization
- Matrilineal Organization
- Kinship Terminology
- Religion and Culture
- Ritual
- Revitalization Movements
- Other religious belief
- Taboo and mana
- Religious beliefs in ethnic groups in Myanmar
- Child training and personality
- Child rearing and the social organization
- Male initiation and child training
- Psychological Anthropology
- Interpersonal relations or interaction between individual
- The relation of culture to individual
- Relationship of personality to culture and social structure
- The relation of culture to society
- The personality of Lisu and Ghekho
- The meaning of race
- Biology concept of race
- Problems with the concept of race
- The social construction of race
- Race and society
- Founders
- The Nature of Culture
- The Nature of Society
- Critique, Limitations and Strength
- The aims of research from anthropological point of view
- The use of literature evidence
- Interpretation of Data
- Physical anthropological technique
- Cultural anthropological technique
- Kind of political systems
- -Uncentralized political systems
- -Centralized political systems
- Formal and Informal Sanctions
- Political Organization and the maintenance of order
- -Internalized control
- -Externalized control
- Anthropological approach to social control
- An Anthropological definition of Law
- Definition of Ethnology
- Historical Background of Ethnology
- Ethnological Field work
- -Ethnological Research and Strategies
- -Analysis of Ethnological Data
- The sub-disciplines of Anthropology
- What is Ethnography?
- The Basic field of Ethnography
- Introduction to Ethnography
- Ethnic Foundation
- Ethnographic enquiry
- Map of a Block
- Private Language
- Body Language
- Ritual
- The Big Ethnography
- Twentieth-Century Evolutionism
- Cultural Materialism
- Critique, Limitations and Strengths
- Structures, Symbols and Meaning
- Criticism of Symbolic Anthropology
- Structures, Practice, Agency
- Materialism versus Culturalism
- Methods and techniques of anthropological research
- -Choice of Informants
- -Sampling
- -Types of documentation
- -Recording; equipment and technique, Collecting and packing
- -Period of field research
- -Analysis Data
- -Research report
- Local group’s reaction to outsiders among food-gatherers and hunter
- Political societies among simpler forming societies
- Types of offences
- Democratic government and undemocratic government
- The goal of government and similarities between political sysems
- The classification of government forms
- Variables Studied by Ethnologists
- -Subsistence and Physical Environment
- -Demography
- -Technology
- -Economy
- -Social Structure
- -Political Organization
- -Religion
- Cross Cultural Research
- Urbanization
- Process of Urbanization
- Demographic change
- The Anthropology and Urban Asia
- Urban ways of life
- The media and Change in the process of Social Change
- Roles in Urban and Rural Communities
- Urban Change and Development
- The Urban Crisis
- The meaning of Social Organization
- Basic Social Groups: Sex, Age grade, Class and Caste, Occupation, Locality
- Marriage
- Preferential Mating
- Extra Marital Relation
- Rules and Restriction of Marriage
- Ways of Acquiring a Wife
- Divorce
- Definition of Religion
- Anthropological approach to religion
- Origins of belief and variation in religious systems
- Religious Practitioners
- Magic and Religion
- Organization of Religion
- Anthropological use of the term “Culture”
- Anthropological use of the term “Personality” and “Character”
- Culture and Individual
- Basic personality
- Modal personality
- Group personality
- Normal personality and abnormal personality
- National Character
- Dependence Training
- The Development of personality
- Factors Producing Human Variation
- Biological Variation in Human Population
- Racial Approach to Variation
- Forms of Family
- Residence Patterns of Extended Family
- Kinship and Descent
- Patrilineal Organization
- Matrilineal Organization
- Kinship Terminology
- Religion and Culture
- Ritual
- Revitalization Movements
- Other religious belief
- Taboo and mana
- Religious beliefs in ethnic groups in Myanmar
- Child training and personality
- Child rearing and the social organization
- Male initiation and child training
- Psychological Anthropology
- Interpersonal relations or interaction between individual
- The relation of culture to individual
- Relationship of personality to culture and social structure
- The relation of culture to society
- The personality of Lisu and Ghekho
- The meaning of race
- Biology concept of race
- Problems with the concept of race
- The social construction of race
- Race and society
- Founders
- The Nature of Culture
- The Nature of Society
- Critique, Limitations and Strength
- A definition of Sociology: The study of Groups
- Group and subgroup
- Characteristics of societies
- Institutionalization, conformity, and social control
- Conformity and specificity of the Norm
- Role conflict and deviation
- Relations between groups
- Structure and function
- Level of social structure
- Kind of political systems
- -Uncentralized political systems-Centralized political systems
- Formal and Informal Sanctions
- Political Organization and the maintenance of order
- -Internalized control-Externalized control
- Anthropological approach to social control
- An Anthropological definition of Law
- Definition of Ethnology
- Historical Background of Ethnology
- Ethnological Field work
- -Ethnological Research and Strategies
- -Analysis of Ethnological Data
- Types of Economic System
- Division of Labor
- Patterns of Production
- Patterns of Distribution
- Property and Ownership
- The sub-disciplines of Anthropology
- What is Ethnography?
- The Basic field of Ethnography
- Introduction to Ethnography
- Ethnic Foundation
- Ethnographic enquiry
- Map of a Block
- Private Language
- Body Language
- Ritual
- The Big Ethnography
- Twentieth-Century Evolutionism
- Cultural Materialism
- Critique, Limitations and Strengths
- Structures, Symbols and Meaning
- Criticism of Symbolic Anthropology
- Structures, Practice, Agency
- Materialism versus Culturalism
- Culture and Socialization
- Culture
- Socialization
- Local group’s reaction to outsiders among food-gatherers and hunter
- Political societies among simpler forming societies
- Types of offences
- Democratic government and undemocratic government
- The goal of government and similarities between political sysems
- The classification of government forms
- Variables Studied by Ethnologists
- -Subsistence and Physical Environment
- -Demography
- -Technology
- -Economy
- -Social Structure
- -Political Organization
- -Religion
- Cross Cultural Research
- Economic Organization
- System of Production
- System of Exchange
- System of Distribution
- System of Consumption
- The Changing Story of Ethnography
- Ethnographic Perspectives
- Expressions of Ethnography
- Collecting, Making, Analyzing Ethnographic data
- Writing an Ethnography
- Choice of ethnic group, area, topic
- Reliability and Incentives of Informants
- Document and Record
- Ethnic relation in selected countries
- The nature of Tourism
- What is Tourist
- Tourist behavior
- Cultural Tourism
- Tourism and Ethnicity
- Cultural Heritage Management and Tourism
- Cultural Tourism Products
- Cultural Tourism Market
- Aim and Scope of Medical Anthropology
- Anthropological approach to Health
- Socio-Cultural context of Health
- Case study (Indigenous Medicine/ Western Medicine)
- Palaeolithic and Neolithic Culture of India
- Palaeolithic and Neolithic Culture of Pakistan
- Palaeolithic and Neolithic Culture of China
- Palaeolithic and Neolithic Culture of Indonesia
- Ethnography and interpretive Anthropology
- Rural life
- Village life
- Strategies for rural development
- Some villages in South East Asia
- The aims of research from anthropological point of view
- The use of literature evidence
- Interpretation of Data
- Physical anthropological technique
- Cultural anthropological technique
- Definition of Cultural Ecology
- A history of thought on Culture and Environment
- The rise of Cultural Ecology
- Defining Cultural within a Tourism Context
- Cross-Cultural differences in rules of Social interaction
- Tourism information and Communication Systems in border Areas
- Social Identities: Movement of Tourism
- Tourism and Social identities
- Culture, Globalization and Tourism
- Contexts of Tourism Development
- Medical Anthropological theories
- Uses of Pharmaceuticals
- Health seeking behaviors
- Self-care
- Applied Medical Anthropology
- Palaeolithic and Neolithic Culture of Malaysia
- Palaeolithic and Neolithic Culture of Vietnam
- Palaeolithic and Neolithic Culture of Thiland
- Prehistoric Culture of Europe
- Prehistoric Culture of Africa
- Urban, Sub-urban, Rural Life
- Urban versus Rural Life
- Rural Life
- Rural Life and village life
- The Death and Life of a small community
- Urbanism
- The development of the American City
- Reasons for the Rapid Growth of Cities
- The Suburbs
- Growth of the Suburbs
- Advantages of Suburbs Life
- Disadvantages of Suburbs Life
- Quality of Life
- People in Cities
- Neighboring
- Production
- leisure
- Choice of Informants
- Sampling
- Types of documentation
- Recording; equipment and technique, Collecting and packing
- Period of field research
- Analysis Data
- Research report
- Anthropology and Cultural Ecology
- Types of adaptation
- Levels of subsistence
- Ecological Systems
- Case Studies
- The Concept of Culture
- Special Fields in Cultural Anthropology
- Patterns of Culture
- The Role of Symbolic behaviour in Culture
- Feminist Anthropology
- Gender Studies
- Introduction to Sociology
- Definition of Sociology
- Nature of Sociology
- Scope of the Sociology
- States in Socialization
- Resocialization
- Gender Socialization
- Political Socialization
- Factor of Social Change
- Resistance To Change
- Environment
- Sustainable Development
- Current scope of Physical Anthropology
- The idea of evolution before Darwin
- The Theory of Natural Selection
- Darwin’s Theory of Evolution
- Gegor Mendel’s Experiments
- Genes: The Conveyors of Inherited Traits
- Original of New Species
- Understanding Humans and Hunan Problems
- Cultural anthropology
- Culture and material reality
- Cultural reproduction theory
- Anthropology in economic development
- Anthropology in business
- Anthropology in health care
- The Concept of Culture
- Special Fields in Cultural Anthropology
- Patterns of Culture
- The Role of Symbolic behaviour in Culture
- Feminist Anthropology
- Gender Studies
- Introduction to Sociology
- Definition of Sociology
- Nature of Sociology
- Scope of the Sociology
- States in Socialization
- Resocialization
- Gender Socialization
- Political Socialization
- Factor of Social Change
- Resistance To Change
- Environment
- Sustainable Development
- The Impact of Social Change on the Environment
- Economic anthropology
- Economics and Economic Anthropology
- Economic Behavior in the Total Perspective of culture
- Systems of Production
- Systems of Exchange
- Property Concept
- System of Consumption
- Social control
- Public Opinion
- Kinds of Political Organization
- Political Societies
- Government and States
- The Concept of Culture
- Special Fields in Cultural Anthropology
- Patterns of Culture
- The Role of Symbolic behaviour in Culture
- Feminist Anthropology
- Gender Studies
- Introduction to Sociology
- Definition of Sociology
- Nature of Sociology
- Scope of the Sociology
- States in Socialization
- Resocialization
- Gender Socialization
- Political Socialization
- Factor of Social Change
- Resistance To Change
- Environment
- Sustainable Development
- The Impact of Social Change on the Environment
- What is research?
- When to use historical research
- Classification according to statistical contents
- Genealogical Method
- Benefits and Precautions in Qualitative Research
Field Works
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |