Categories
 Department of English
Department of English
 |
Dr Ei Ei Soe Min Head of Department Professor Ph.D (Linguistics) Department of English, Yadanabon University, Mandalay, Myanmar (+95-09) eisoemin@gmail.com |
Staff
| Professor | – | 1 |
| Associate Professor | – | 5 |
| Lecture | – | 6 |
| Assistant Lecturer | – | 5 |
| Tutor | – | 9 |
| Office Staff | – | 1 |
| Total | – | 27 |
History of the Department
Flipping through the historical background of the Department of English, it comes along side with Yadanabon University which was established as Liberal Arts and Sciences University in 2000. There are many professors who served as Head of the English Department since the University was founded. Some of the former Heads of the Department who have served from the year 2004 are: U Tiin Aung, Daw Tin Myat Yee, Daw Lay Lay Mi, Dr. Khin Ma Ma Tin, Daw Myint Myint, Dr. Pa Pa Sein, Dr. Mon Mon Wai.
The department focuses on students’ acquisition of English language and the appreciation of English literature. Students have opportunities to learn English literature, linguistics, communicative skills, research methodology and approaches and methods of English language teaching. Students who specialized in English could study English Language and Literature as a course, in addition, Myanmarsar, Philosophy, Oriental Studies, International Relations and History are parts of foundation and elective courses as well. Students could admit to degree programmes such as BA (English), BA (Honors English), MA Qualifying, and MA (English).
Many proficient students who drive positive change for the country and the community have been produced. Moreover, the Department of English always tries to improve the quality of teachers and students. Teachers motivate students to involve in English language competition, Language boost camp, workshop and other Campus activities. On the other hand, to enhance the proficiency and capacity of the teachers, the department conducts teacher training and refresher courses. Teachers are also eager to do research. In addition, English Department is actively participating in various activities of the University.
Vision
- To ensure that students develop creativity and critical thinking skills
- To maintain balance between the needs of learning English language from the global perspectives and interdisciplinary studies
- To offer students adequate communication skills in preparation for their professional needs in the globalized scenario prevalent today
Mission
- To provide English learners with the opportunities to acquire knowledge and skills that can be applied to find their true vocation as well as profession
- To enhance students’ ability to appreciate English literature and enable them to use English language through sustainable quality education
Programs Offered
| BA. / BA. (Hons) in English |
| MA. in English |
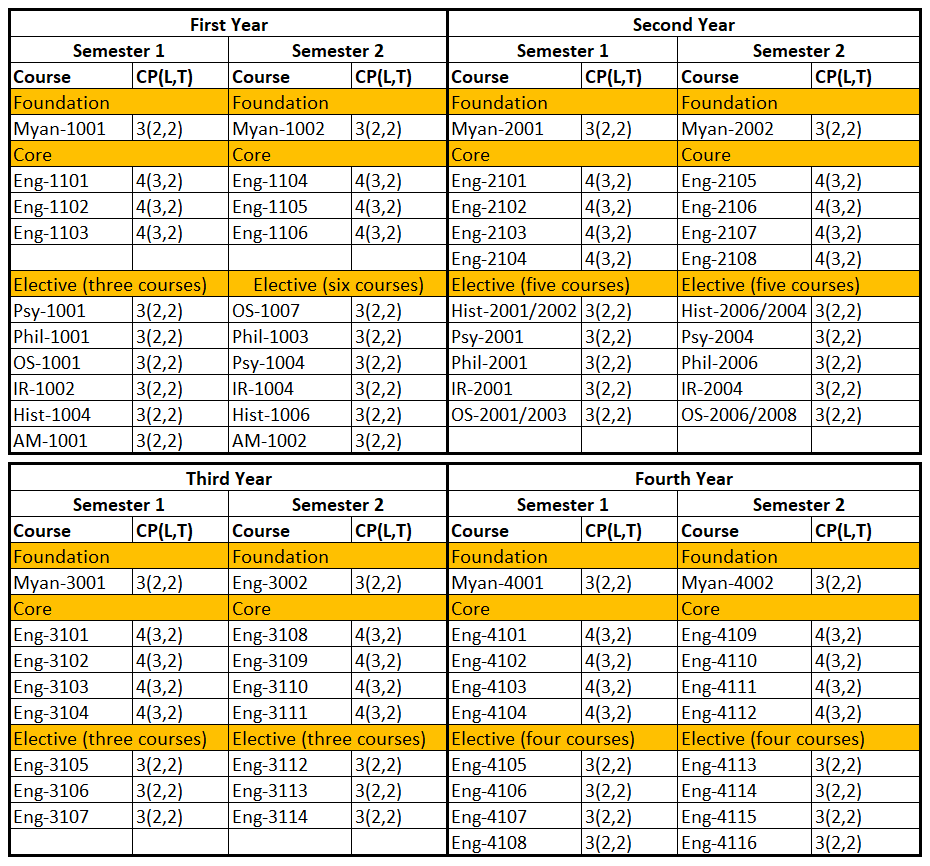
Curriculum
BA in English
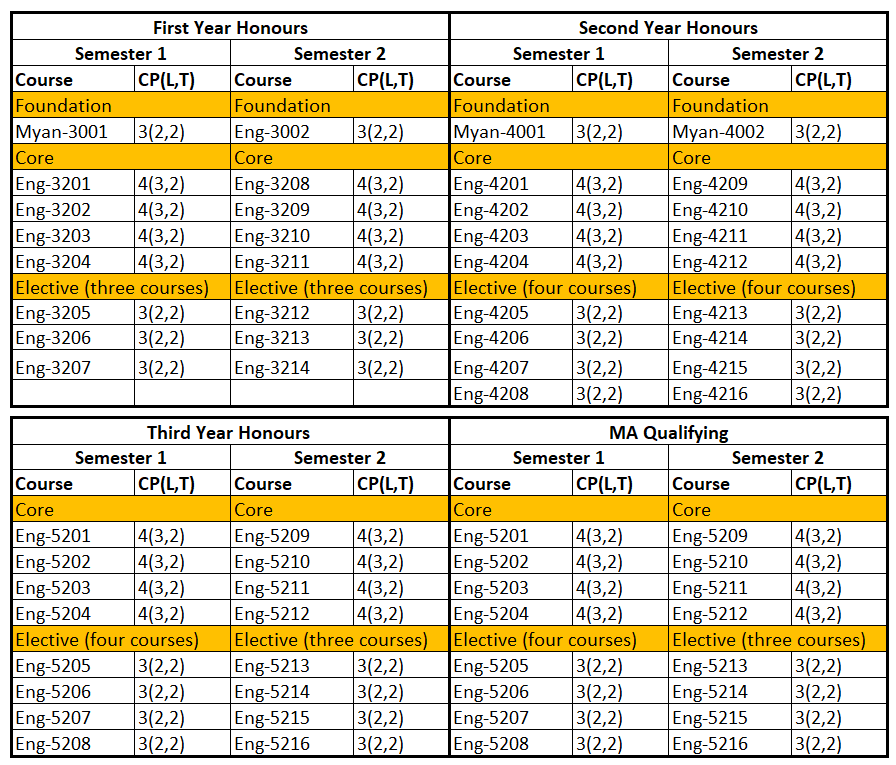
BA. (Hons) in English
Students who passed second year with GPA greater than 4 are eligible to attend BA. (Honours) classes for three years. After finished successfully, they are earned BA. (Hons) degree majoring in English.
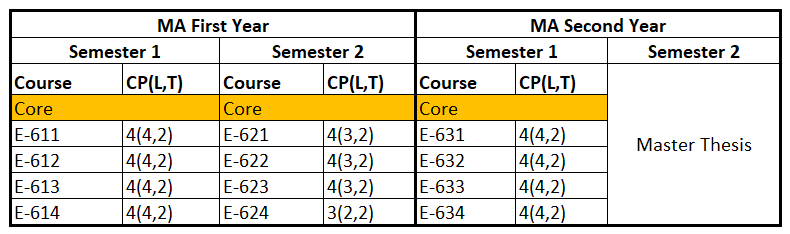
MA in English
Descriptions Modules Offered
This module introduces students to English literature through selected 19th& 20th century prose passages and short stories by well-known authors in the 20th century. The selection includes various themes. This module will help students to understand the various types of prose passages and style of writing and characteristics of short stories such as plot, setting, mode of development, and literary devices.
Prose writing and short stories being mirrors of a particular period or age, these selections will raise students’ awareness of the historical, social and cultural background of the story. This module will also train students to read literary texts closely, and appreciate them and express their understanding of texts both in class discussion and in writing.
This module deals with 20th century Poetry and Drama. It will help students to become acquainted with the language and various styles of literary texts and enable them to gain knowledge of the social economic and educational aspects of that period as reflected in these texts. A selection from the 20th century poetry includes a rich variety of poems, both British and American, which are representative of the period, being selected and presented through a thematic approach. It aims at helping students to appreciate the poems in modern English. In the process of studying them, it is hoped that students’ language skills will be enhanced.
This module also offers selections from 20th century English Drama. It enables students to read not only for pleasure but also to understand life as presented by these playwrights. This module includes the plays, written in a variety of styles, for the stage, making it possible for them. It makes it possible for students to study plays to get a glimpse of play-acting and the theatre from the mid-nineteenth century to the present, encompassing such radical movements as realism, naturalism and symbolism. It also introduces them to the theatre of the absurd, and post-modernism.
The vocabulary component aims at developing students’ ability to infer meaning from words as used in the context and in building up their vocabulary.
The grammar component serves as a good reference for students on a variety of sentence structures which will help students improve their reading as well as writing skills.
Presentations of advanced grammar points will give students a solid base for learning English and help them communicate with great accuracy.
The reading component familiarizes students with a variety of texts followed by different types of exercises that develop students’ information gathering skills, thinking ability, extract immediate responses and develop their literal as well as inferential comprehension skills.
The writing component provides students with a firm foundation in academic writing and in writing formal, informal and business letters and writing academic papers.
The speaking component first provides students with useful expressions that can be used in different social, academic and business contexts which are followed by activities that enable them to communicate effectively without inhibition and also stimulate them to talk about a variety of thought-provoking topics.
The listening component provides students with opportunities to learn to listen through authentic listening materials that make use of real information from a variety of sources to promote understanding.
Moreover, the exercises require the students to extract the main ideas and specific details and help them improve their pronunciation.
This module introduces students to literature through a selection of 16th to 20th century prose passages and short stories by well-known writers in these centuries. The selection has various themes. This module helps students to understand the style of various types of prose passages and the characteristics of short stories such as plot, setting, mode of development, and literary devices. As short stories are mirrors of a certain age, the selection helps the students to gain knowledge about the author’s life, and the historical, social and cultural background of the story. This module trains students to read literary texts intensively and to express their understanding of these texts both in class discussion and in writing.
This module deals with the study of a rich variety of poems, both British and American, which are representative of the century, being selected and presented in a thematic approach. Students will be able to appreciate the selected poems expressed in modern English so that their language power in speaking and writing will be enhanced.
This module also deals with selections from English Drama of19th&20th centuries. Students will be able to read not only for pleasure but also to tackle conventional themes in the light of a new understanding of the theory and development of tragedy, comedy, and other modes of dramatic expression. It aims at helping students to develop their language through an intensive study of the style of writing in these plays, which introduce the on-setting element of modernism.
This module introduces general linguistics and phonetics to learners of English. The first part consists of the definition of language, the origin and the development of language, characteristics and varieties of language, as well as animal and human language. It also focuses on the definition, the scope of linguistics, types of linguistics and its related fields. The second part deals with the definition of phonetics, its branches, and the description of vowels and consonants.
The module deals with two sub-disciplines in linguistics which concerns with sound, namely phonetics and phonology. It also describes the International Phonetic Alphabet, English consonants and vowels, and vowel phonemes. Moreover, it focuses on the smallest of the superordinate units, the syllable and the phonological units above the syllable such as the phonetic characteristics of stress, stress position, segmental phonology of the phrase and word.
The vocabulary component aims at developing students’ ability to infer meaning from words as used in the context and in building up their vocabulary.
The grammar component serves as a good reference for students on a variety of sentence structures which will help students improve their reading as well as writing skills.
Presentations of advanced grammar points will give students a solid base for learning English and help them communicate with great accuracy.
The reading component familiarizes students with a variety of texts followed by different types of exercises that develop students’ information gathering skills, thinking ability, extract immediate responses and develop their literal as well as inferential comprehension skills.
The writing component provides students with a firm foundation in academic writing and in writing formal, informal and business letters and writing academic papers.
The speaking component first provides students with useful expressions that can be used in different social, academic and business contexts which are followed by activities that enable them to communicate effectively without inhibition and also stimulate them to talk about a variety of thought-provoking topics.
The listening component provides students with opportunities to learn to listen through authentic listening materials that make use of real information from a variety of sources to promote understanding.
Moreover, the exercises require the students to extract the main ideas and specific details and help them improve their pronunciation.
This module includes a selection of 19th and 20th century English short stories and novels. Short stories are studied with particular attention to setting, plot, characterization, literary devices, climax, point of view, theme, symbols, conflicts, and development of the story. Thismodule will enhance the students’ ability to gain full understanding of the writer’s message and to appreciate literature from different points of view.
The novels in the 19th and 20thcenturies were particularly engaged with the events, circumstances, beliefs and attitudes of their time. It concentrates on a critical study of works by the centuries’ major literary figures like E.M. Foster, G.K. Chesterton, Joseph Conrad, Virginia Woolf, Ernest Hemingway, etc. This module places their works in the contexts in which they were written and read.
This module first deals with the study of a rich variety of poems, which are presumably representative of 18th and 19th century poetry, being selected and presented through a thematic approach. Students will be able to extend their knowledge of English poetry that they had already garnered, going mentally backward into the past centuries in their academic pursuit. Students pursue their scholarly studies in English poetry, perceiving how English poetry had developed over the centuries.
This module then studies a variety of approaches to the question of drama in the eighteenth century: as a field of literary practice and a type of theatrical performance. Students, studying society comedy, will be able to observe how the conventional elements of farce are transformed into satiric epigrams, questioning Victorian social values and norms staged in the setting of the theatre; how eighteenth-century intellectuals think through the relationship between dramatic form and the social world; and how eighteenth-century drama mobilizes new images of gender and the family. It aims to acquaint students with the major works of Richard Brinsley Sheridan, Oscar Wilde, Bernard Shaw, and Oliver Goldsmith.
This module acquaints learners of English with some background concepts of words and rules of word formation. Moreover, it also deals with morphemes:free and bound morphemes, lexical and functional morphemes, inflectional versus derivational morphology, and morphological analysis.
This module concerns preliminaries to syntactic structure such as the goals of syntactic theory, the importance of syntactic theory, introduction to constituent structure, ways of representing constituent structure, investigation of constituent structure and phrasal categories. It also deals with types of syntactic rules, the relation between rules and sentences. Moreover, it also looks at the subcategorization through different approaches such as the Aspects approach, Principles and Parameters (P&P) approach and Phrase Structure Grammar (PSG) approach.
This module deals with the theoretical aspect of translation and translation studies, the background history of translation, general types of translation, features of a good translation, and directives by different translators. It trains students to apply their theoretical knowledge to the practice of translation. It also focuses on conceptual bases required to understand both the principles and recurrent issues and difficulties in professional translation and interpreting.
This module deals with the theoretical aspect of the process of translating and translation procedures. Students will be able to put their theoretical knowledge into practice through the translation of lexis, proper names, idioms and proverbs, abbreviations and acronyms, first at the sentence level, and then at the paragraph level. It also focuses on basic theoretical components in interpreter and translator training, similarities and differences between interpreting and translation.
The vocabulary component aims at developing students’ ability to infer meaning from words as used in the context and in building up their vocabulary.
The grammar component serves as a good reference for students on a variety of sentence structures which will help students improve their reading as well as writing skills.
Presentations of advanced grammar points will give students a solid base for learning English and help them communicate with great accuracy.
The reading component familiarizes students with a variety of texts followed by different types of exercises that develop students’ information gathering skills, thinking ability, extract immediate responses and develop their literal as well as inferential comprehension skills.
The writing component provides students with a firm foundation in academic writing and in writing formal, informal and business letters and writing academic papers.
The speaking component first provides students with useful expressions that can be used in different social, academic and business contexts which are followed by activities that enable them to communicate effectively without inhibition and also stimulate them to talk about a variety of thought-provoking topics.
The listening component provides students with opportunities to learn to listen through authentic listening materials that make use of real information from a variety of sources to promote understanding.
Moreover, the exercises require the students to extract the main ideas and specific details and help them improve their pronunciation.
This module covers all the four language learning skills, grammar points and vocabulary that are used in business communication. It also focuses on different areas of business that closely reflect business undertakings. It aims to develop students’ spoken and written English, enabling them to use it accurately and appropriately. Students will be able to develop their language skills as well as the content knowledge regarding respective business functions.
This module offers a general knowledge of business English for the functions of marketing. It aims to develop students’ four language skills for use in a professional environment. Students learn the language for presenting which is essential to make a point in business functions. Students will be able to make logical connections between ideas and concepts in a given text or texts, give instructions and make suggestions regarding business information.
This module deals with studying and researching language to increase knowledge of the English language system. It also focuses on teaching pronunciation techniques and the assessment of students’ performance and giving feedback.
This module enables the students to get through their first research projects successfully and without wasting lots of time in trial and error. It also helps the students to develop sound techniques and good practice which will serve them well in future research projects. It focuses on writing a research paper systematically with the correct format. It enhances the students’ understanding of the different approaches to research studies, making decisions on the appropriate approach to any research they undertake and critically evaluating information, data and sources.
This module offers students a selection of the 19th century short stories and the novel with particular attention to Maria Edgeworth, Nathaniel Hawthorne, Frank R. Stockton, Edgar Allan Poe and Guy de Maupassant. It centers on the critical reading of the selected short stories and the novels enabling students to develop conceptual learning and the critical thinking skills.
This module also deals with the evolution of the nineteenth-century novel as it moves from Jane Austen’s pastorals to the ruder ones of Thomas Hardy, exploring ways in which the novel reflects, soothes, and intensifies the unspoken tensions within its culture. This module traces the disruptive pressure of increasingly powerful women and the intensifying pull of the past, which becomes more difficult to resist as modernity takes shape. This module focuses on the works concerned with social comedy and satire of the period, the 19th century. It concentrates on the works of Oscar Wilde, Jane Austen, Emily Bronte, Thomas Hardy, etc.
This module will look at the behaviour of reflexives and reciprocals (known as anaphora) within P&P and PSG frameworks. It will also familiarize students with a variety of sentence types which involve either Noncanonical complements or subjects and canonical complements or subjects and they will be analysed through the monostratal approach (PSG) and multistratal approach (P&P). Moreover, it is also concerned with the notions of subject and object and how they are defined within the frameworks of Lexical Functional Grammar (LFG), Relational Grammar (RG) and Transformational Grammar (TG). Moreover, this module also aims to introduce students to the area of Semantics which includes the meaning of Semantics, lexical and grammatical meaning, and different semantic theories.
This module familiarizes students with the analysis of passives and raising sentences using the classical transformational approach and P&P approach. It also discusses the main differences and the relation between P & P and PSG. Moreover, in this module, students will be provided with the definition of discourse, discourse versus text, types of discourse, interpreting discourse, linguistic elements in discourse such as cohesion, coherence, and conversation analysis.
This module focuses on the methods and procedures of translation and interpretation. It imparts the knowledge and use of strategies of translation and interpretation. Students are trained through practicing on collocation, cohesion at the paragraph level, textual and discourse level. Students will be able to do interpreting through an approach of discourse processing and interpreting strategies.
This module trains the students at the paragraph level, textual and discourse level by giving practical exercises from extracts of different genres to improve their translation skills and interpreting skills. It links practices and concepts in translation and interpretation and concepts and theories from cognitive psychology and psycholinguistics.
This module introduces students to the study of ASEAN Literature in English and provides them with the knowledge of ASEAN culture and a firm foundation of approaches to literary study. The focus is on the different genres of literary works from ASEAN countries. This module covers a wide range of socio-cultural aspects in South East Asia countries such as people, family ties and values, growing up, festivals, and so on. It helps students to gain a critical appreciation of the writer’s craft through close textual study and through social aspects. It also enhances students’ exploration of themes, characterization, setting, plot and point of view.
The vocabulary component aims at developing students’ ability to infer meaning from words as used in the context and in building up their vocabulary.
The grammar component serves as a good reference for students on a variety of sentence structures which will help students improve their reading as well as writing skills.
Presentations of advanced grammar points will give students a solid base for learning English and help them communicate with great accuracy.
The reading component familiarizes students with a variety of texts followed by different types of exercises that develop students’ information gathering skills, thinking ability, extract immediate responses and develop their literal as well as inferential comprehension skills.
The writing component provides students with a firm foundation in academic writing and in writing formal, informal and business letters and writing academic papers.
The speaking component first provides students with useful expressions that can be used in different social, academic and business contexts which are followed by activities that enable them to communicate effectively without inhibition and also stimulate them to talk about a variety of thought-provoking topics.
The listening component provides students with opportunities to learn to listen through authentic listening materials that make use of real information from a variety of sources to promote understanding.
Moreover, the exercises require the students to extract the main ideas and specific details and help them improve their pronunciation.
This module aims to develop students’ presentation and communication skills to be better able to communicate in a business environment. It also focuses on Business English required for their future work in sales and marketing. Students will be able to learn language skills, acquire knowledge in business grammar and vocabulary to master formal written and oral communication in various aspects of business English.
This module introduces theoretical background to the practice of English language teaching. Moreover, it provides methodologies for developing language skills: receptive and productive skills. It also deals with classroom management and tackling the problem behaviour of learners.
This module deals with methodology for developing productive skills. It also concerns new ideas in making lesson plans and the testing and the evaluation of students.
This module enables students to speak clearly and confidently in different situations – in classrooms, in careers and in communities. It aims at developing students’ oral communication skills– speaking and listening – and written communication skills – reading and writing. It presents principles with applications, emphasizing audience-centered communication so that students can learn how to talk toand with themand not at them. This module also provides students with key skills for effective presentation such as useful language expressions, voice and delivery, rhetorical techniques and question handling.
This module includes a selection of 19th and 20th century English short stories and novels. Short stories are studied with particular attention to setting, plot, characterization, literary devices, climax, point of view, theme, symbols, conflicts, and development of the story. This module will enhance the students’ ability to gain full understanding of the writer’s message and to appreciate literature from different points of view.
The novels in the 19th and 20thcenturies were particularly engaged with the events, circumstances, beliefs and attitudes of their time. It concentrates on a critical study of works by the centuries’ major literary figures like E.M. Foster, G.K. Chesterton, Joseph Conrad, Virginia Woolf, Ernest Hemingway, etc. This module places their works in the contexts in which they were written and read.
This module first deals with the study of a rich variety of poems, which are presumably representative of 18th and 19th century poetry, being selected and presented through a thematic approach. Students will be able to extend their knowledge of English poetry that they had already garnered, going mentally backward into the past centuries in their academic pursuit. Students pursue their scholarly studies in English poetry, perceiving how English poetry had developed over the centuries.
This module then studies a variety of approaches to the question of drama in the eighteenth century: as a field of literary practice and a type of theatrical performance. Students, studying society comedy, will be able to observe how the conventional elements of farce are transformed into satiric epigrams, questioning Victorian social values and norms staged in the setting of the theatre; how eighteenth-century intellectuals think through the relationship between dramatic form and the social world; and how eighteenth-century drama mobilizes new images of gender and the family. It aims to acquaint students with the major works of Richard Brinsley Sheridan, Oscar Wilde, Bernard Shaw, and Oliver Goldsmith.
This module acquaints learners of English with some background concepts of words and rules of word formation. Moreover, it also deals with morphemes:free and bound morphemes, lexical and functional morphemes, inflectional versus derivational morphology, and morphological analysis.
This module concerns preliminaries to syntactic structure such as the goals of syntactic theory, the importance of syntactic theory, introduction to constituent structure, ways of representing constituent structure, investigation of constituent structure and phrasal categories. It also deals with types of syntactic rules, the relation between rules and sentences. Moreover, it also looks at the subcategorization through different approaches such as the Aspects approach, Principles and Parameters (P&P) approach and Phrase Structure Grammar (PSG) approach.
This module deals with the theoretical aspect of translation and translation studies, the background history of translation, general types of translation, features of a good translation, and directives by different translators. It trains students to apply their theoretical knowledge to the practice of translation. It also focuses on conceptual bases required to understand both the principles and recurrent issues and difficulties in professional translation and interpreting.
This module deals with the theoretical aspect of the process of translating and translation procedures. Students will be able to put their theoretical knowledge into practice through the translation of lexis, proper names, idioms and proverbs, abbreviations and acronyms, first at the sentence level, and then at the paragraph level. It also focuses on basic theoretical components in interpreter and translator training, similarities and differences between interpreting and translation.
The vocabulary component aims at developing students’ ability to infer meaning from words as used in the context and in building up their vocabulary.
The grammar component serves as a good reference for students on a variety of sentence structures which will help students improve their reading as well as writing skills.
Presentations of advanced grammar points will give students a solid base for learning English and help them communicate with great accuracy.
The reading component familiarizes students with a variety of texts followed by different types of exercises that develop students’ information gathering skills, thinking ability, extract immediate responses and develop their literal as well as inferential comprehension skills.
The writing component provides students with a firm foundation in academic writing and in writing formal, informal and business letters and writing academic papers.
The speaking component first provides students with useful expressions that can be used in different social, academic and business contexts which are followed by activities that enable them to communicate effectively without inhibition and also stimulate them to talk about a variety of thought-provoking topics.
The listening component provides students with opportunities to learn to listen through authentic listening materials that make use of real information from a variety of sources to promote understanding.
Moreover, the exercises require the students to extract the main ideas and specific details and help them improve their pronunciation.
This module covers all the four language learning skills, grammar points and vocabulary that are used in business communication. It also focuses on different areas of business that closely reflect business undertakings. It aims to develop students’ spoken and written English, enabling them to use it accurately and appropriately. Students will be able to develop their language skills as well as the content knowledge regarding respective business functions.
This module offers a general knowledge of business English for the functions of marketing. It aims to develop students’ four language skills for use in a professional environment. Students learn the language for presenting which is essential to make a point in business functions. Students will be able to make logical connections between ideas and concepts in a given text or texts, give instructions and make suggestions regarding business information.
This module deals with studying and researching language to increase knowledge of the English language system. It also focuses on teaching pronunciation techniques and the assessment of students’ performance and giving feedback.
This module enables the students to get through their first research projects successfully and without wasting lots of time in trial and error. It also helps the students to develop sound techniques and good practice which will serve them well in future research projects. It focuses on writing a research paper systematically with the correct format. It enhances the students’ understanding of the different approaches to research studies, making decisions on the appropriate approach to any research they undertake and critically evaluating information, data and sources.
This module offers students a selection of the 19th century short stories and the novel with particular attention to Maria Edgeworth, Nathaniel Hawthorne, Frank R. Stockton, Edgar Allan Poe and Guy de Maupassant. It centers on the critical reading of the selected short stories and the novels enabling students to develop conceptual learning and the critical thinking skills.
This module also deals with the evolution of the nineteenth-century novel as it moves from Jane Austen’s pastorals to the ruder ones of Thomas Hardy, exploring ways in which the novel reflects, soothes, and intensifies the unspoken tensions within its culture. This module traces the disruptive pressure of increasingly powerful women and the intensifying pull of the past, which becomes more difficult to resist as modernity takes shape. This module focuses on the works concerned with social comedy and satire of the period, the 19th century. It concentrates on the works of Oscar Wilde, Jane Austen, Emily Bronte, Thomas Hardy, etc.
Eng 4203 & 4211: English Language Studies
This module will look at the behaviour of reflexives and reciprocals (known as anaphora) within P&P and PSG frameworks. It will also familiarize students with a variety of sentence types which involve either Noncanonical complements or subjects and canonical complements or subjects and they will be analysed through the monostratal approach (PSG) and multistratal approach (P&P). Moreover, it is also concerned with the notions of subject and object and how they are defined within the frameworks of Lexical Functional Grammar (LFG), Relational Grammar (RG) and Transformational Grammar (TG). Moreover, this module also aims to introduce students to the area of Semantics which includes the meaning of Semantics, lexical and grammatical meaning, and different semantic theories.
This module familiarizes students with the analysis of passives and raising sentences using the classical transformational approach and P&P approach. It also discusses the main differences and the relation between P & P and PSG. Moreover, in this module, students will be provided with the definition of discourse, discourse versus text, types of discourse, interpreting discourse, linguistic elements in discourse such as cohesion, coherence, and conversation analysis.
This module focuses on the methods and procedures of translation and interpretation. It imparts the knowledge and use of strategies of translation and interpretation. Students are trained through practicing on collocation, cohesion at the paragraph level, textual and discourse level. Students will be able to do interpreting through an approach of discourse processing and interpreting strategies.
This module trains the students at the paragraph level, textual and discourse level by giving practical exercises from extracts of different genres to improve their translation skills and interpreting skills. It links practices and concepts in translation and interpretation and concepts and theories from cognitive psychology and psycholinguistics.
This module introduces students to the study of ASEAN Literature in English and provides them with the knowledge of ASEAN culture and a firm foundation of approaches to literary study. The focus is on the different genres of literary works from ASEAN countries. This module covers a wide range of socio-cultural aspects in South East Asia countries such as people, family ties and values, growing up, festivals, and so on. It helps students to gain a critical appreciation of the writer’s craft through close textual study and through social aspects. It also enhances students’ exploration of themes, characterization, setting, plot and point of view.
The vocabulary component aims at developing students’ ability to infer meaning from words as used in the context and in building up their vocabulary.
The grammar component serves as a good reference for students on a variety of sentence structures which will help students improve their reading as well as writing skills.
Presentations of advanced grammar points will give students a solid base for learning English and help them communicate with great accuracy.
The reading component familiarizes students with a variety of texts followed by different types of exercises that develop students’ information gathering skills, thinking ability, extract immediate responses and develop their literal as well as inferential comprehension skills.
The writing component provides students with a firm foundation in academic writing and in writing formal, informal and business letters and writing academic papers.
The speaking component first provides students with useful expressions that can be used in different social, academic and business contexts which are followed by activities that enable them to communicate effectively without inhibition and stimulate them to talk about a variety of thought-provoking topics.
The listening component provides students with opportunities to learn to listen through authentic listening materials that make use of real information from a variety of sources to promote understanding.
Moreover, the exercises require the students to extract the main ideas and specific details and help them improve their pronunciation.
This module aims to develop students’ presentation and communication skills to be better able to communicate in a business environment. It also focuses on Business English required for their future work in sales and marketing. Students will be able to learn language skills, acquire knowledge in business grammar and vocabulary to master formal written and oral communication in various aspects of business English.
This module introduces theoretical background to the practice of English language teaching. Moreover, it provides methodologies for developing language skills: receptive and productive skills. It also deals with classroom management and tackling the problem behaviour of learners.
This module deals with methodology for developing productive skills. It also concerns new ideas in making lesson plans and the testing and the evaluation of students.
This module enables students to speak clearly and confidently in different situations – in classrooms, in careers and in communities. It aims at developing students’ oral communication skills– speaking and listening – and written communication skills – reading and writing. It presents principles with applications, emphasizing audience-centered communication so that students can learn how to talk toand with themand not at them. This module also provides students with key skills for effective presentation such as useful language expressions, voice and delivery, rhetorical techniques and question handling.
This module motivates students to analyse, criticize and evaluate literature systematically through the close study of the 19th century short stories; someEnglish novelsof the 18thcentury; a rich variety of English poetry selections, which are presumably representatives of 16th, 17th&18th century; and Modern European drama from the 16thto 18th century to the present. It enables students to improve critical thinking skills and creativity so that the students would be able to apply their knowledge and skills gained from studying literature to their everyday life.
This module covers such topics as language and verbal communication across cultures; non-verbal communication across cultures; cultural influences on the expression and perception of emotions; identity and intergroup communication; communication in intercultural relationships; and adapting to an unfamiliar culture. It also looks at how people from differing cultural backgrounds communicate, in similar and different ways among themselves, and how they cope with the task of communicating across cultures.
This module deals with two branches of Applied Linguistics: Sociolinguistics and Psycholinguistics. In sociolinguistics, students will learn language variation such as code, dialect, sociolect, idiolect, registers, diglossia, pidgin and creole, language contact and language change, etc. In Psycholinguistics, students will have knowledge of what Psycholinguistics means, and first language acquisition, second language acquisition/ learning and different theories of language acquisition.
This module introduces stylistics and pragmatics to students of English. Stylistics consists of main concepts and definitions of stylistics such as the scope of stylistic study, the definitions of style and stylistics, and stylistic analysis. In Pragmatics, students will learn how people use language within a context and why they use language in particular ways. It also deals with such topics as deixis, reference, implication, presupposition, speech acts, politeness, and rules of conversation.
This module will equip students with important skills that they will need at work: negotiation and meeting skills. Effective negotiating component will provide students with the language they need to hand the typical scenario encountered on the way to successful negotiations. Effective meetings will present all the speaking skills that they students in order to participate in a meeting with confidence. It will also provide them with expressions needed in typical everyday business meetings.
This module will improve students’ communication skills at work and their language knowledge in key areas of the media. It will also give students opportunity to discuss the media topic, to participate in listening activities reflecting media scenarios, realistic speaking activities, reading and writing practices based on authentic media documents and engage them in topics and articles which ensure that learning is interesting and motivating.
This module deals with short story, poetry, drama, prose and the novel ranging from 17th century to 20th century, written by writers of great prominence: Russia, France, China, India, Japan, Nigeria, Vietnam, Chile, Spain, South Korea, Norway, Germany, and America. Students are introduced to a rich variety of selections both from the East and the West, written in a variety of styles so that they will get a panorama of the World Literature.
The vocabulary component aims at developing students’ ability to infer meaning from words as used in the context and in building up their vocabulary.
The grammar component serves as a good reference for students on a variety of sentence structures which will help students improve their reading as well as writing skills.
Presentations of advanced grammar points will give students a solid base for learning English and help them communicate with great accuracy.
The reading component familiarizes students with a variety of texts followed by different types of exercises that develop students’ information gathering skills, thinking ability, extract immediate responses and develop their literal as well as inferential comprehension skills.
The writing component provides students with a firm foundation in academic writing and in writing formal, informal and business letters and writing academic papers.
The speaking component first provides students with useful expressions that can be used in different social, academic and business contexts which are followed by activities that enable them to communicate effectively without inhibition and also stimulate them to talk about a variety of thought-provoking topics.
The listening component provides students with opportunities to learn to listen through authentic listening materials that make use of real information from a variety of sources to promote understanding.
Moreover, the exercises require the students to extract the main ideas and specific details and help them improve their pronunciation.
This module aims to improve students’ English language skills within a business context for handling different situations in doing business. It also offers general knowledge of business English. Students will improve their knowledge of communication skills and use English effectively in the professional working environment.
This module focuses on developing business communication skills in work-related activities and language skills. Students will be exposed to a greater variety of business-related vocabulary and various types of business news, letters and reports in the modern business world. They will be able to employ suitable business communicative strategies and communicate ideas more effectively within a business context.
This module deals with the language of tourism and aims to develop students’ essential skills related to hotel and tourism industries. It also aims to develop effective listening and speaking skills with a wide range of communicative practices. Reading and writing skills also feature prominently and functional language is also presented in context.
This module is a skill-based course which provides lots of language activities to help students develop the essential skills needed for hotel and tourism. It also helps learners become aware of communicative needs of tourism professionals. It provides further work on reading, writing, grammar, functions and vocabulary related to tourism topics.
Grammar and language teaching: Correlates of Grammar and language teaching, Traditional grammar, Taxonomic grammar, Phrase structure grammar, Transformational grammar, Case grammar, Prepositional and modal information in a grammar, Halliday’s functional grammar, Transformational and systemic models of grammar, Communicative competence, Functional grammar and functional language teaching.
Differences between linguistics and sociolinguistics
Key Terms: Speech, Speech Community, Language Community, Dialect (Regional, Social, Temporal)
Language contact & Language change: Bilingualism (Stable/Unstable), Pidgin, Creole, Lingua franca, External change (Borrowing, Loan translation), Internal change (Coining, Combining, Extending)
Speech event, Speech factors, Speech functions, Paralinguistic behavior, Code switching
Approach to teaching prose, Analysing language, Analysing prose style, Comparing the different prose styles of various texts.
A brief history of language teaching, The Grammar-Translation Method; Language teaching innovations in the nineteenth century, The reform movement, The Direct Method; The nature of approaches and methods in language teaching: approach, design, procedure; The Audiolingual Method: background, approach, design, procedure, the decline of Audiolingual Method.
Designing a Research Study: Introduction (The nature of research), Qualitative research, Quantitative
research, Conclusion (Course evaluation: combining research types)
Writing a Research Paper: Proposal writing, Outlining, Abstract, Introduction, Literature Review, Conclusion, Bibliographies, Citing Sources, Paraphrasing, Summarizing and Quoting.
The study of learners’ language: Error Analysis: Lapses, mistakes and errors, Expressive and receptive errors, The practical uses of error analysis;
Attitudes towards errors: Aims and uses of error analysis, Aims of research workers Aims of teachers, syllabus designers and materials writers;
Data for error analysis: Both correct and incorrect instances should be included, Data from individuals or groups, Variety of data;
The significance of learners’ errors: The process of error analysis, Recognition, Interpretation, Reconstruction, Linguistic classification;
Explanation of causes: Interlingual causes of errors, Intralingual causes of errors, Cross-association, Wrong analogy and over-generalization, Other possible causes of errors, Carelessness, Other errors ‘encouraged’ by teaching.
Non-contrastive approach to error analysis: Types and causes of intralingual and developmental errors, Over-generalization, Ignoranceof rule restriction, Incomplete application of rules, False concepts Hypothesized
Remedial work: The need for remedial teaching, Selection of problem areas for remedial work, Errors for incidental correction, Selecting errors for more intensive remedial work.
Psycholinguistics
Introduction: View of language from psycholinguistic perspective, Criteria for correct language usage, Behaviorist views of language
Paragraph Structure, Narrative Paragraphs, Descriptive paragraphs, Process paragraphs, Comparison /Contrast paragraphs, Essay Organization, Opinion Essays, Argumentative Essays, Critique Writing (Book reviews) and Concise Writing.
What is stylistics? The need for stylistics; The concern of stylistics; Levels of analysis;
Dimensions of situational constraint: individuality, dialect, time, discourse, province, status, modality, singularity
Semantic Theories: The semiotic triangle, Collocational theory, Structural semantics, Componential analysis, The projection problem, Generative and interpretive, semantics, Pedagogic considerations, Further reading
Reading
What do we know about the process of second language reading?: In what ways is reading an interactive process?, In what ways is reading a purposeful process?, In what ways is reading a critical process?, What is the role of extensive reading?
What are the implications for the teaching of reading?: How do we establish goals for the reading classroom?, What criteria do we use to select reading texts?, What kinds of tasks help to develop reading ability?
Listening
What do we know about the listening process?: Bottom-up processes in listening, Top-down processes in listening, Purposes for listening
What uncertainties exist for foreign language listeners?: Uncertainties of confidence, Uncertainties deriving from the presentation of speech, Uncertainties because of gaps in the message, Uncertain strategies, Uncertainties of language, Uncertainties of content, Visual uncertainties
What are the implications for the English Language classroom?: Creating reasons for listening, Selecting texts for listening, Designing listening activities for the classroom, Building confidence in listening to English, Conclusion
Speaking
What is involved in speaking English competently?: Distinguishing types of speaking situation, Making oneself understood, Managing interaction
What are the issues in teaching phonological aspects of English?: Choosing a model for pronunciation teaching, Taking a holistic or atomistic approach, Selecting practice according to student need
What are the implications for classroom practice in the teaching of spoken English?: Talking with students about spoken English, Making accuracy-based practice meaningful, Providing a range and balance fluency-based activities
Teaching the pronunciation component of a course: Managing classroom interaction, Conclusion
Writing
What do we know about the process of writing? : What strategies do skilled writers use as they compose?
What activities characterize the writing process?: Managing interaction, What are the implications of a process approach?, Helping students to generate ideas, Providing practice in planning, Contextualizing tasks to develop a sense of audience, Encouraging students in revision strategies, Supporting students with technology, Issues in introducing a process approach
How can we analyse and describe the structure of written texts?: What are the implications of a text-based approach to writing?, Helping students to identify their writing needs, Building awareness of discourse organization, Helping students to develop crafting skills, Enabling students to appreciate the criteria for an effective text, Conclusion
Developing Literary Skills
Using literature in the language classroom: The issues, What is literature?, What is distinctive about the language of literature?, The reader and the text, Literary competence and the language classroom, Why use literature in the language classroom?
Approaches to using literature with the language learner: An overview, A language-based approach to using literature, Stylistics in the classroom, Literature as content: How far to go?, The role of metalanguage
Selecting and evaluating materials: Selecting texts, Evaluating learning materials which make use of literary texts
Reading literature cross-culturally: Being a student, A consideration of cultural aspects in texts, Strategies for overcoming cultural problems
Materials design and lesson planning: Novels and short stories: Writing your own story, Distinctive features of a short story, Anticipating student problems when using a short story, Planning a lesson for use with a short story, Further tasks and activities for use with a short story, Designing your own materials for use with a short story, Using novels in the language classroom
Materials design and lesson planning: Poetry: Putting a poem back together again, What is distinctive about poetry?, Why use poetry with the language learner?, Exploiting unusual language features, Helping students with figurative meanings, Using poetry with lower levels, Using poetry to develop oral skills, Using a poem with students at higher levels, Anticipating student problem, Further tasks and activities
Materials design and lesson planning: Plays: What is distinctive about play?, The language of a play, The performance of a play, Why use play in the language learning classroom?, Using play extracts to think about language in conversation, Using play extracts to improve students’ oral skills, Using play extracts with lower levels, Anticipating student problem, Further activities for play extracts, Using a whole play with students
Reflecting on the literature lesson: Thinking about observation, General observation of the literature lesson, Micro-tasks for reflecting on specific areas of teaching, Observing a student, Other ways of monitoring your teaching
The origin of language curriculum development: Historical background; Vocabulary selection; Grammar selection and gradation; Assumptions underlying early approaches to syllabus design;
From syllabus design to curriculum development: Changing needs for foreign languages; Communicative language teaching; Emergence of a curriculum approach in language teaching;
Needs analysis and situation analysis: Needs analysis; Situation analysis;
Planning goals and learning outcomes: The ideology of the curriculum; Stating curriculum outcomes; Non-language outcomes and process objectives;
Course planning and syllabus design: The course rationale; Describing the entry and exit level; Choosing course content; Determining the scope and sequence; Planning the course structure; Preparing the scope and sequence;
Evaluation: Evaluating textbooks; Evaluating student progress; Evaluating the programme
Beginning and development of the Novel, Features of the novel (general); Theme, plot, character, characterization, development of the prescribed novels: The Great Gatsby; Things Fall Apart
Beginning of Drama, Survey of Drama, Types of Drama: Comedy, tragedy; Features of Drama;
Shakespeare’s tragedies: Macbeth; Analysing acts and scenes; Analysing language; Dealing with plot, characterization, and development of the play
Testing for Language Teachers
Teaching and testing: backwash, inaccurate tests, the need for tests, what is to be done;
Testing as problem solving: an overview of the book;
Kinds of test and testing: proficiency tests, achievement tests, diagnostic tests, placement tests, direct versus indirect testing, discrete point versus integrative testing, norm-referenced versus criterion-referenced testing, objective testing versus subjective testing, communicative language testing;
Validity: content validity, criterion-related validity, construct validity, face validity, the use of validity; Reliability: the reliability coefficient, the standard error of measurement and the true score, scorer reliability, how to make tests more reliable, reliability and validity;
Achieving beneficial backwash;
Stages of test construction: statement of the problem, providing a solution to the problem