Categories
 Department of History
Department of History
 |
Dr Tun Tun Shein Head of Department-History Professor Ph.D (History) Department of History, Yadanabon University, Mandalay, Myanmar (+95-09) Tuntunshein774@gmail.com |
Staff
| Professor | – | 2 |
| Associate Professor | – | 4 |
| Lecture | – | 1 |
| Assistant Lecturer | – | – |
| Tutor | – | 9 |
| Office Staff | – | 1 |
| Total | – | 17 |
History of the Department
The origin of the Department of History in the Yadanabon University started in the academic year 2000-2001. Professor U Myat Ni was behind the establishment of the Department. The department of History offers B.A, B.A (Hons) and M.A Degree.
Vision
- The vision of history department is to promote human resources by teaching social, political, economic and culture history and to cultivate their patriotic spirit.
Mission
The Department of History has a mission to
- Understand students the development of human civilization
- Train to love Myanmar custom and tradition
- Support history students in their day to day academic problems.
Programs Offered
| BA. / BA. (Hons) in History |
| MA. in History |
Curriculum
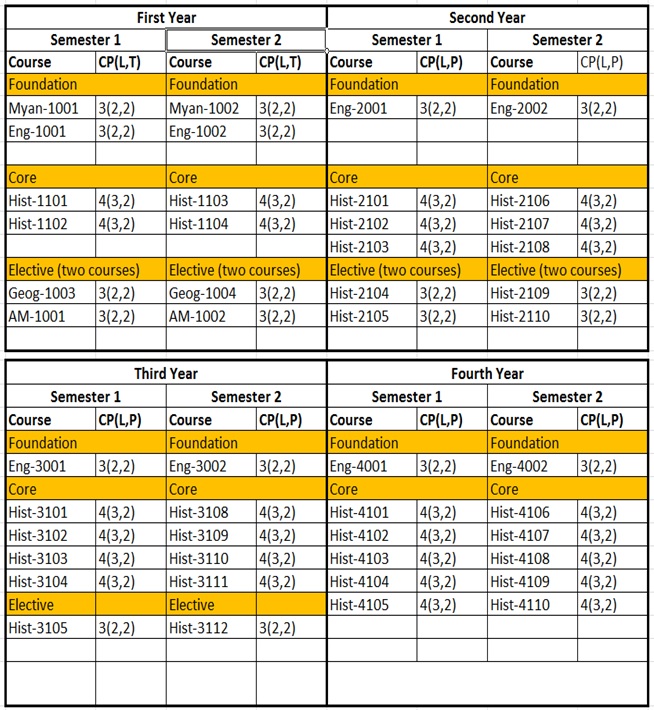
BA in History
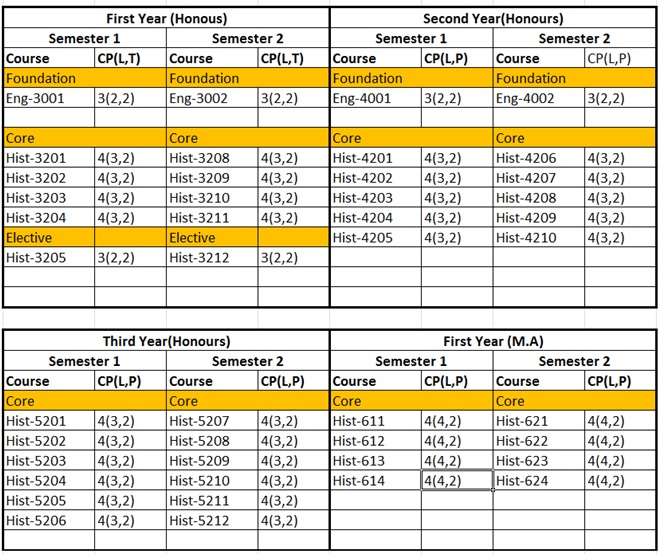
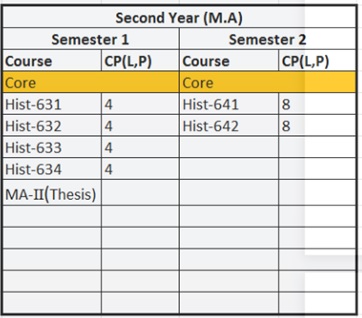
B.A (Hons:) & M.A in History
Students who passed second year with GPA greater than 4 are eligible to attend B.A. (Honours) classes for three more years. After finished successfully, they are earned B.A. (Hons:) degree majoring in History.
Students who passed with B.A (Honours) first class (or) second class (first division) (or) second class (second division) are eligible to attend M.A classes for two more years. After finished successfully, they are earned M.A degree majoring in History.
Descriptions Modules Offered
The purpose of this module is to enable students to understand the basic concepts of psychology. Students will learn, in the first semester, the nature, origin and methods of psychology. In addition, the module provides with the importance of biological bases of behaviour, sensation and perception in human behaviour, states of consciousness and learning. In the second semester, students will learn the human memory, motivation, emotion, intelligence, and personality which are factors related to the behaviour of human.
- The nature of child development
- Early Childhood
- Middle and Late Childhood
- The Nature of Adolescence and Physical Development
- Cognitive Development in Adolescence
- Social Development in Adolescence
- Adolescence Problem, Stress, Health, and Coping
- The Nature of Adolescence and Physical Development
- Cognitive Development in Adolescence
- Social Development in Adolescence
- Adolescence Problem, Stress, Health, and Coping
- The Nature of Adolescence and Physical Development
- Cognitive Development in Adolescence
- Social Development in Adolescence
- Adolescence Problem, Stress, Health, and Coping
- The Nature of Adolescence and Physical Development
- Cognitive Development in Adolescence
- Social Development in Adolescence
- Adolescence Problem, Stress, Health, and Coping
- The Nature of Adolescence and Physical Development
- Cognitive Development in Adolescence
- Social Development in Adolescence
- Adolescence Problem, Stress, Health, and Coping
- Introduction to Developmental Psychology
- Growth and Development
- Key Areas of Development
- Healthy vs faulty development
- Nature, Scope and Methods of Educational Psychology
- Individual Differences
- Learning in the Classroom
- The Psychology of the Teacher
- Applying Psychology in Your Life
- Psychology in Home Life
- Mental Health and Guidance
- Psychological Counselling
- Psychology in Health and Medicine
- Psychology in Industry and Business
- Psychology Applied to Crime
- Psychology Applied to Environment
- The Scope of Experimental Psychology
- Psychophysics
- Attention
- Perception
- Reaction time and association
- Learning
- Conditioning
- Retention and Forgetting
- Transfer of Training
- Language Acquisition
- Language Production and Comprehension
- Models and Explanations of Human Thought
- The Relationship between Language and Thought
- What is Stress?
- Stressor
- Stress Responses
- Stress, Illness and health
- Coping with Stress
- The Development of Self in Infancy
- The Development of Self in Middle Childhood
- Self- esteem and Identity in Adolescence
- The Cultural Context of Self
- The individual and Personality
- Social and Cultural Context
- Cultural Differences in Pro- social Behavior
- Selection, Placement and Training
- Determinants of Effectiveness in Occupation
- Motivation Workers for Optimum performance
- Attitudes and Behavior
- Evaluating Job Performance
- Job Satisfaction and Analyzing Turnover
- Leadership in Occupation
- Occupational Stress
- Counseling Skill for Managers
- Careers in Organizations
- Scope and Methods of social Psychology
- Cultural and Personality
- Social Motives
- Social Perception
- The Behavior of Group s
- Leadership
- The Nature and Measurement of Attitudes
- Interacting with others
- Introduction to I\ O Psychology
- Criteria of Job Performance
- Job Analysis
- Personnel Selection
- Job Satisfaction
- Employee Motivation to Work
- Organizational Culture
- Leadership in Organization
- Conflict Management in Organizations
- The Nature and scope of Abnormal Psychology
- Classification of Mental disorders
- Dissociative (Somatoform) Disorders
- Anxiety Disorders
- Schizophrenia
- Paranoid Disorders
- Mood Disorders
- Anti- social Personality Disorders
- Psychological Treatment and Services
- Introduction Frequency Descriptive
- Measures of Central Tendency
- Measures of Variability
- Cumulative Distribution and Norms
- The Normal Distribution Curve
- Correlation (Pearson)
- Special Correlation Techniques
- Hypothesis Testing
- Testing about Population means
- Testing about Differences between Two Uncorrelated means
- Testing about Differences between Two Correlated means
- Testing the Differences between Percentages
- Non- Parametric Statistics
- Chi square
- Who are Criminal?
- Testimony and the Courtroom
- Biological Paradigms
- Psychiatric Paradigms
- Social- Psychological Theories
- Sociological Tradition- Normative Paradigms
Psy 3111/ 3211: Crime and Psychology II
- Psychology and Legal System
- Forensic Psychology
- Mental Disorder and Its Legacy
- Divancy
- Aggression- Definition and Causes of Aggression
- Preventing or Changing Aggressive Behavior
- 1What is Community Psychology
- Understanding Sense of Community
- The Methods of Community Research
- Understanding Coping and Social Support
- The Concepts of Development and Ageing
- Biological Aspects of Adult Development and Ageing
- Psychological Aspects of Adult Development Ageing
- Sociological Aspects of Adult Development and Ageing
- Who are Criminal?
- Testimony and the Courtroom
- Biological Paradigms
- Psychiatric Paradigms
- Social- Psychological Theories
- Sociological Tradition- Normative Paradigms
- Psychology and Legal System
- Forensic Psychology
- Mental Disorder and Its Legacy
- Divancy
- Aggression- Definition and Causes of Aggression
- Preventing or Changing Aggressive Behavior
- An Overview of Counseling
- Theories of Counseling
- Counseling Process
- Skills Used in Counseling Relationship
- Personal Approach to Counseling
- Group Counseling
- Comparison to Individual and Family Counseling
- Children and Adolescence Counselling
- Introduction to Sport Psychology
- Personality and the Athlete
- Attention in Sport
- The Effects of Arousal, Anxiety and Audience on Performance
- Motivation in Sport
- Leadership and Team Cohesion in Sport
- Aggression in Sport
- Psychological Techniques for Improving Performance
- Function and Origins of Psychological Testing
- Principle Characteristic of Test
- Social and Ethical Implications of Testing Reliability
- Validity
- Norms
- General Intelligence Test
- Aptitudes Tests
- Personality Assessments
- Measures of Interest and Attitude
- Situitional Tests
- The Role and Importance of Research
- Different Type of Research
- Formulation of Research Objectives and Hypotheses
- Samples and Population
- The Use of Theory
- Research Designs
- Quantitative Methods
- Qualitative Methods
- Mixed Methods Procedures
- Communicating the Results of Research in Psychology
- Basic Principles of Ethical Research (add)
- Introduction to Health Psychology
- Psychological and Behavior Therapies in Health Psychology
- Nature of Stress
- Coping Methods
- Psychological Mechanisms of Health and Disease
- Healthy Lifestyle Behaviors I (Food and Exercise)
- Healthy Lifestyle Behaviors ( The Invisible Drugs)
- Pain and Health Psychology
- Approaches to the Study of Social Problems
- Family- Related Problems
- Poverty
- The Sexes and Social Inequality
- Age and Social Inequality
- Health Care
- Crime and Delinquency
- Alcohol and Drug Abuse
- Communication
- Personnel Training
- Performance Appraisal
- Human Engineering
- Managing Job Stress
- Altruism
- Aggression
- Conformity
- Groupthink? Group Processes? Group Dynamics?
- Contemporary Perspectives of Abnormal Behavior
- Cause of Abnormal Behavior
- Psychosocial Factors in Physical Illness
- Personality Disorders
- An Introduction to Organizational Behavior
- Theories of Organization
- Groups in Organization
- Intergroup Conflict
- Construction of Theories as a Psychological process
- Pavolov’s Classical Conditioning
- Skinner’s Operant Conditioning
- Recent Development in Cognitive Theoriest
- Clinical Assessment
- Interview and Psychological tests
- Psychotherapy
- Biologically based Therapy
- The Research Process
- The Measurement Process
- Research Design
- Some Conventional Research Design Types
- Neuroanatomical Basis of Behavior
- Sensition
- Brain and Consciousness
- Sleeping and Working
- Learning and Remembering
- Emotion
- The Field of Social Psychoclogy
- Person Perception
- Self- Perception
- Attitudes
- Nature of Cultural Psychology
- Nature of Culture
- Culture and Mental Process
- Culture and Social Behavior
- Health related Research
- Coping with Illness
- The role of Health Care Professional
- Drug Addiction
- Ecology and Population
- Effects of Environmental Factors on Behavior
- Effects of Human Behavior on the Environment
- Spaces and Social Interaction
- 1Aptitude and Special Ability Tests
- Achievement tests and the Assessment of Learning Disabilities
- Psychological Measurement in Industry
- Drug Addiction
- What is Qualitative research?
- Qualitative Research and Secondary Analysis
- Survey Research
- Participant Observation
- Nature of Intelligence Testing
- Measuring Multiple Aptitudes
- Personality Inventories
- Measures of Interest and Value
- Projective Techniques
- Situational Tests
- Systems Approach
- Organizations Development
- Decision- Making in Organizations
- Design of Jobs
- Management of Pooe Performance
- Reward Systems
- Psychodynamic Theories
- Social Learning Theories
- Phenomenological Theories
- Dispositional Theories
- Obedience
- Competition and Cooper
- Structural Aspects and Elementary Processes in Groups
- Decision Making in Group
- Intergroup Conflicts
- Creating Counselling and Therapy Approaches
- Psychodynamic Therapies
- Humanistic – Existential Therapies
- Cognitive Behavior Therapies
- Recent Therapies
- Multicultural and Gender Therapies
- An Overview of Psychology and Health
- Enhancing Health and Presenting Illness
- Psychological Problems of Hospitalized Patients
- Chronic Health Problems
- Evaluating Behavioral Interventions in Hospitals
- Perceptual Organization
- Theories of Perception
- Individual, Social and Cultural Variations in Perceptual Organization
- The Development of Perceptual Process
- The Nature of Social Research
- Qualitative Social Research
- Quantitative Social Research