Categories
Science Department of Geology
Department of Geology
Staff
| Professor | – | 2 |
| Associate Professor | – | 1 |
| Lecture | – | 3 |
| Assistant Lecturer | – | 1 |
| Tutor | – | 4 |
| Total | – | 11 |
History of the Department
History of the Department
The origin of the Department of Geology in the Yadanabon University started in the academic year 2000-2001. Rector U Win Maung and Pro-rector U Than Nwe were behind the establishment of the Department. The department of Geology offers BSc, BSc (Hons) and MSc the programmes in Geology.
Vision
- To provide the high level of education with well trained, competent, academic and professional geologists
Mission
- The department of Geology strives to provide the natural resource development and management of the environmental problem through education and research program in geology
Programs Offered
| BSc / BSc (Hons) in Geology |
| MSc in Geology |
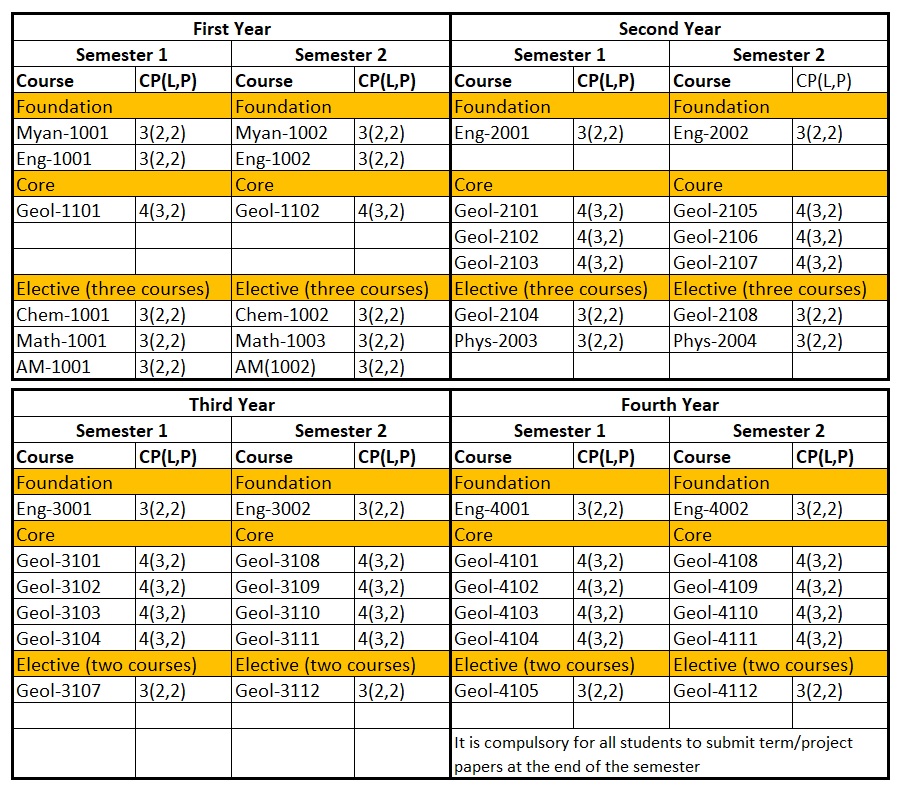
Curriculum
BSc in Geology
BSc (Honours) in Geology
Students who passed second year with GPA greater than 4 are eligible to attend B.Sc. (Honours) classes for three more years. After finished successfully, they are earned B.Sc. (Hons) degree majoring in Geology.
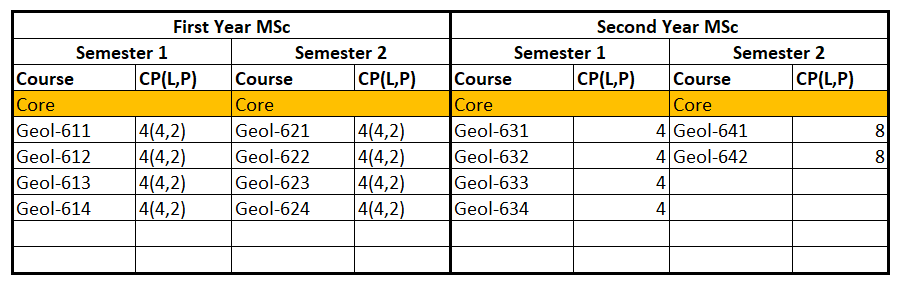
MSc in Geology
Students who passed second year with GPA greater than 4 are eligible to attend MSc classes for two years. After finished successfully, they are earned MSc degree majoring in Geology.
Descriptions Modules Offered
- The Earth: Geology and its uses; The Earth’s internal structure and composition, age, and origin.
- Earth Materials: Minerals and their properties; Common rock-forming minerals; Common ore minerals; Igneous rocks; Sedimentary rocks; Metamorphic rocks; The rock cycle.
- Earth Processes: External Geological Processes: Weathering; Geological works of running water, groundwater, mass movements, the sea, wind and ice.
Practical Work
Mineral properties; Common rock-forming and ore minerals; Common igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic rocks; Topographic maps
References
- Skinner, B.J. & S.C. Potter (1992), The Dynamic Earth (2nd. Edn.)
- Foster, R.J. (1988), General Geology (5th. Ed)
3. ဒေါက်တာဉီးသိန်း (၁၉၇၈) အထွေထွေဘူမိဗေဒ
- Earth Process: External Geological Process: Weathering; Geological works of running water, groundwater, mass movements, the sea, wind and ice.
- Earth’s Internal Geological Processes: Folding; Faulting; Jointing; Formation
of Unconformities; Volcanism; Seismicity; Orogeny; Plate Tectonics.
- Earth History: Radiometric Dating; Geological Time Scale; Fossils and Fossilization; Evolution of life.
- Earth Resources: Mineral Deposits; Fossil Fuels; Brief account mineral deposits of Myanmar.
Practical Work
Block diagrams; Geological Maps
References
- Skinner, B.J. & S.C. Potter (1992), The Dynamic Earth (2nd. Edn.)
- Foster, R.J. (1988), General Geology (5th. Edn.)
3. ဒေါက်တာဉီးသိန်း (၁၉၇၈) အထွေထွေဘူမိဗေဒ
- Crystallography: Elements of symmetry; Crystal notations; Stereographic projection; Common crystal classes and common forms; Twinning in crystal.
- Crystal chemistry: Bonding; Major Silicate Structures; Bonding; mineralogical relations: chemical variations (Ionic substitution, solid solution, Isomorphism), structural variations (polymorphism)
Practical Work
- Study of common crystal forms; Miller Indices; Stereographic Projection.
- The polarizing microscope; Optical properties of minerals.
References
- READ, H.H., (1976) Rutley’s Elements of Mineralogy. (26th. Edn.)
- Brownlow, A.H., (1979) Geochemistry
3. Wade, F.A & R. A Maltox, (1960). Elements of Crystallography and Mineralogy
- Definition & Scope
- Bedding and its recognition; top and bottom determination
- Mechanical properties; forces, stress and strain, factors controlling behavior of materials
- Types of deformation and mechanics of plastic deformation
- Fractures; tensional fractures and shear fractures, compression fractures, extension fractures, Joint, genetic classification of joints, interpretation of joint diagrams, etc.
- Mechanics of folding; description and classification of folds; types of fold
- Mechanics of faulting, description and classification of faults, normal fault, strike-slip fault, reverse fault, thrust fault and overthrust, criteria for recognition of faults
- Morphotectonics and lineaments
Practical Work
Determination of true and apparent dips, Outcrop pattern and structural block diagrams, Joint diagram; Construction of cross-sections.
References
Park R.G. (1983) Foundations of Structural Geology, 1st publication, Blackies & Son Limited
Billings, M. P., (1972). Structural Geology (2nd. Edn.)
Badgley, P.C., (1959). Structural Methods for Exploration Geologists
Pluijm, B.A.D. and Marshak, S., (1997). Earth,s Structure: An Introduction to Structural Geology Tectonic
FIELD GEOLOGY
- Scope, importance; uses
- Methods of observations and measurements:
Use of topographic maps and air-photos; tape-and-compass traverse method; outcrop mapping; outcrop procedures; sampling and collecting; recording
- Field work with sedimentary rocks
- Field work with igneous rocks
- Field work with metamorphic rocks
- Preparation of Geological maps and cross-sections
- Writing Geological reports
SURVEYING
- Scope, definations, and applications; Types of surveying; Instruments
- Linear and angular measurements
- Chain / tape surveying
- Compass surveying (by prismatic, Brunton and clinometers compasses)
- Levelling
Practical Work for Field Geology
Exercises on the uses of Geological compasses, traverse method, joint rose diagrams, stereographic projection of planar and linear structures; Study of Geological maps and cross-sections.
Practical Work for Surveying
Linear and angular measurements; Chain / tape surveying; Alidade surveying; Levelling; Volume of earthwork and calculations.
References
- Compton, R.R. (1985) Geology in the Field (2nd Ed.)
- Davis, R. E. (1955) Elementary Plane Surveying (3rd. Ed.)
3. Kissam, P. (1956) Surveying (2nd Ed.)
- Introduction: General Consideration, Environmental Geology – An Overview; Environmentalism
– Fundamental Concepts of Environmental Geology
– Earth System; Earth Resources
2. Geologic Hazards: Hazards from earthquakes and tsunamis; Hazards from ground failures, Hazards from volcanic eruptions; Expansive soils; their causes and mitigation
3. Hydrologic Hazards: Hazards from floods, Coastal hazards, their causes and mitigation
Tutorial / Practical
- Causes and mitigation on natural Geologic and hydrologic hazards, earth resources
References
- Keller, E. A. (1988) Environmental Geology (5th Ed.)
- Murck, B. W., B. J. Skinner and S. C. Porter (1996). Environmental Geology
- Hays, W.W (Ed) (1981). Facing Geologic and Hydrologic Hazards (USGS Pub.)
- ADPC, (2009). Hazards Profiles in Myanmar
- Principles of Optical Mineralogy: Nature and properties of light; Polarizing microscope; Optical properties of minerals (under orthoscope and conoscope); Preparation of thin sections
- Systematic Mineralogy: Classification; Physical and optical properties of olivine, pyroxene, amphibole, mica, feldspar, feldsparthoid, silica groups, and other important minerals and mineral groups (Garnet, Tourmaline, Carbonate, Aluminosilicate groups, etc)
- Important Gem Minerals: Physical properties of diamond, ruby, sapphire, emerald, aquamarine, peridot, jadeite
Practical Work
Megascopic and microscopic studies of common and important minerals
References
- Read, H.H., (1976). Rutley’s Elements of Mineralogy (26th. Ed.)
- Kerr, P.F., (1977) Optical Mineralogy (4th. Ed.).
- Cleavage and schistosity; origin, relation of cleavage and schistosity to major structures
- Secondary lineation: origin, types of secondary lineation, relation of lineation to major structures
- Structural petrology or Petrofabrics
- Continental drift
- Sea-floor spreading
- Plate tectonics
Practical Work
Stereographic projection of bedding, foliation and lineation, Orthographic and stereographic projection in solving fold and fault problems, Structural contour map, Structural map with faults;
References
R.G. Park, (1983) Foundations of Structural Geology
Billings, M. P. (1972). Structural Geology (2nd Ed.)
Badgley, P.C. (1959). Structural Methods for Exploration Geologists
Pluijm, B .A.D and Marshak, S., (1997) Earth’s structure: An Introduction to Structural Geology and Tectonics
- Human-induced Hazards and Problems: Waste disposal, Soil degradation, erosion and desertification, Their causes and mitigation
- Using and Caring for Earth Resources: Mineral resources, Fossil fuels, Water resources, Land use.
- Protection and Preservation of the Natural Environment in Myanmar: Status of Environmental degradation in Myanmar, Environmental problems facing Myanmar and suggested remedial actions, Environmental education, Policy, and Legislation.
Tutorial / Practical
Tutorials on human-induced Geologic and hydrologic hazards, earth resources, and land use
References
- Keller, E. A. (1988) Environmental Geology (5th Ed.)
- Murck, B. W., B. J. Skinner and S. C. Porter (1996). Environmental Geology
- Hays, W.W (Ed) (1981). Facing Geologic and Hydrologic Hazards (USGS Pub.)
- Miller, G. T. (1998) Environmental Science with working the Earth
5. ADPC, (2009). Hazard Profiles in Myanmar
- Introduction
- Magmatic processes: stages in magmatic consolidation: fractional crystallization and Bowen’ reaction series
- Igneous structures and field relationships
- Textures and microstructures of igneous rocks
- IUGS Classification of Igneous rocks
Practical Work
- Megascopic petrography of igneous rocks of Myanmar.
- Textures and microstructures of igneous rocks in thin section.
References
- Williams, H, F. J. Turner & C. M. Gilbert (1954). Petrography.
- Hatch, F. H., A.K. Wells & M. K. Wells (1972). Petrology of the Igneous Rocks (3rd Ed.)
- Hyndman, D. W., (1985) Petrology of Igneous and Metamorphic Rocks (2nd Ed.)
4. Winter, J. D. (2001). An Introduction to Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology.
- Introduction; Scope; History; Uses
- Processes of sedimentation; Weathering; Erosion; Transportation; Deposition and Depositional Environments; Post-depositional Changes.
- Properties of sediments: Composition; Textures; Structures; Mass properties
- Products of sedimentation; Classification of sedimentary rocks
Practical Work
- Megascopic petrography of common sedimentary rocks
- Size frequency distribution
- Microscopic study of clastic sedimentary rocks
References
- Pettijohn, F. J. (1975). Sedimentary Rocks (3rd Ed.)
- Williams, H., F.J. Turner & C.M. Gilbert (1954). Petrography
- Reineck, H. E. and I. B. Singh (1980). Depositional Sedimentary Environment with Reference to Terrigeneous clastics (Second Revised and Update Edition)
- Blatt, H., G. Middleton, R. Murray (1980) Origin of Sedimentary Rocks (2nd Ed.)
5. Tucker, H. E, (1991) Sedimentary Petrology (2nd Ed.)
- Introduction, meaning and scope.
- Fossils and fossilization.
- Systematic and nomenclature.
- Systematic study of phyla Protozoa, Porifera, Coelenterata, Bryozoa, Graptolithina, mentioning general features, morphological characteristics, classification, paleoecology, and stratigraphic significance.
Practical Work
- Types of fossilization
- Identification and systematic description of selected important genera of phyla Protozoa, Porifera, Coelenterata, Bryozoa and Graptolithina.
References
- Shrock , R. R., & W. H. Twenhofel (1953) Principles of Invertebrate Paleontology
- Moore, R. C., C. G. Lalicker & A. G. Fischer, (1952) Invertebrate Fossils
- Easton, W. H. (1960) Invertebrate Paleontology
4. Clarkson, E. N. K. (1993) Invertebrate Paleontology and Evolution (3rd Ed.)
- Introduction: Scope; History
- Metamorphism: Agents; Processes; Types
- Textures and structures of metamorphic rocks
- Classification of metamorphic rocks
- Metamorphic grades, zones and facies
- Metamorphism of politic, quartzzo-feldspathic, calcareous, magnesian, and basic rocks
- Relationship between regional metamorphism and tectonism
- Metamorphic belts and Epochs of Myanmar
Practical works
- Megascopic petrology of common metamorphic rocks
- Textures of metamorphic rocks
- Microscopic petrology of common metamorphic rocks
References
- Williams, H, F. J. Turner & C. M. Gilbert (1954). Petrography.
- Winter, J. D. (2001) An Introduction to Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology
- Hyndman, D. W., (1985) Petrology of Igneous and Metamorphic Rocks, New York, McGraw Hill, 2nd edition.
- Raymond, L. A (1995). Petrology (igneous, sedimentary, metamorphic rocks)
5. Yardley, B.W. D (1983), An introduction to metamorphic petrology
- Introduction to Geophysics: Physical properties of Rocks and Minerals; Classification of Geophysical Methods; The Geophysical Model; Direct and Indirect Application; Ambiguity in Interpretation.
- The basic principles and practices in Gravity Method: Magnetic method, Electrical method, Resistivity method, Electromagnetic method, Induced polarization method, Radioactive method and seismic method.
Tutorial / Practical Work
- Tutorial on Subfields of Geophysics; Petrophysical properties; Principles of Geophysics; Geophysical methods
References
- Parasnis (1986). Principles of Applied Geophysics, 4th edition.
2. Howell, A. K. : Introduction to Geophysics
- Overview and History of Marine Geology; Internal Structures of the Earth; The earth’s gravity field; The earth’s magnetic field
- Geophysics and Ocean Morphology; The Continental Margin; The Oceanic Ridges; Fracture Zones; The Ocean-Basin Floor; Marginal Trenches; Seismic Reflection; Seismic Refraction
- Ocean Basin Tectonics: Principal Features of Ocean Spreading Centres; Principal Features of Ocean Subduction Zones
- Study of Continental Margins; Passive Continental Margins (Rift Phenomena); Active Continental Margins (Accretionary Prisms)
- Submarine and island arc volcanoes.
Tutorial Work
- Ocean morphology, ocean basin tectonics, continental margins
References
- Kennet, J. P. (1982) Marine Geology, 2nd Edition, New York, Prentice Hall
- Seibold, E., and Berger, W. H., (1996) The Sea Floor: An Introduction to Marine Geology, Springer-Verlag, 3rd Edition, 356p.
- Duxbury A. C. and A. B. Duxbury (1984) An Introduction to World’s Oceans, 2nd Edition
Erickson.J. (2003). Marine geology; Exploring the News frontiers of the ocean.
- Basic concepts of geomorphology; Scale, processes, structural influences, climate, people as geomorphic agents.
- Fluvial processes and their landforms; Streams and valleys; Drainage patterns; Stream meandering; Fluvial cycles; River terraces; Peneplain concept.
- Tectonic and structural landforms; Landforms controlled by faults; Landforms controlled by folds.
- Karst landforms: Surface landforms; Subsurface caves and springs; Karst evolution.
- Coastal processes and landforms: Tides, waves and currents: Eustatic sea-level changes; Erosional and depositional landforms of coasts; deltas and estuaries; Continental shelves and submarine canyons.
- Paleogeomorphology: Relict landforms; Burried landforms; Exhumed landforms.
- Applied geomorphology: Application to Hydrology; Application to economic geology; Application to Engineering projects; Application to oil exploration.
Practical Work
- Interpretation of topographic maps for the purpose of geologic information.
- Interpretation of air-photographs and geological maps.
References
- Thornbury, W.D. (1969). Principles of Geomorphology. (2nd Edn.)
2. Selby, M.J. (1985). Earth’s Changing Surface; An Introduction to Geomorphology.
- Petrography of various clans of the acid, intermediate, basic and ultrabasic groups, pyroclastic rocks and lamprophyres
- Igneous associations at various plate boundaries
- A brief account of igneous activity of Myanmar
- Brief account of the major granitoid belts of Myanmar
- Geological setting of the Central Volcanic Belt
Practical Work
Microscopic petrography of igneous rocks of Myanmar.
References
- Williams, H, F. J. Turner & C. M. Gilbert (1954). Petrography.
- Hatch, F. H., A.K. Wells & M. K. Wells (1972). Petrology of the Igneous Rocks (3rd Edn.)
3. Winter, J. D. (2001). An Introduction to Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology
-
- Clastic sedimentary rocks: Conglomerates and breccias; Sandstones; Siltstones; Shales.
- Chemical and organic sedimentary rocks: Limestones; Dolomites and dolomitization; Chert; Evaporites; Iron formations
- Depositional environments and facies (Environmental analysis)
Practical Work
- Megascopic petrography of common sedimentary rocks of alluvial, deltaic, shallow marine (with tempestite and tsunamites), deep sea and pelagic sedimentation.
- Microscopic petrography of clastic and carbonate sedimentary rocks.
References
- Pettijohn, F. J. (1975). Sedimentary Rocks. (3rd. Edn.)
- Williams, H., F.J. Turner & C.M. Gilbert (1954) Petrography
- Reineck, H. E. and I. B. Singh (1980) Depositional Sedimentary Environment with reference to Terrigeneous clastics, (Second Revised and Update Edition)
- Blatt, H., G. Middleton, R. Murray (1980) Origin of Sedimentary Rocks, 2nd Edition.
5. Tucker, H. E. (1991) Sedimentary Petrology. 2nd Edition.
- Systematic study of phyla Echinodermata, Arthropoda, Brachiopoda, and Mollusca, mentioning general features, morphological characteristics, classification, paleoecology, and stratigraphic importance.
- Introduction to trace fossils.
Practical Work
Study of morphological features, identification and systematic description of selected important genera of phyla Echinodermata, Arthropoda, Brachiopoda and Mollusca and trace fossils.
References
- Shrock , R. R., & W. H. Twenhofel (1953) Principles of Invertebrate Paleontology
- Moore, R. C., C. G. Lalicker & A. G. Fischer, (1952). Invertebrate Fossils
- Easton, W. H. (1960). Invertebrate Paleontology
- Clarkson, E. N. K. (1993). Invertebrate Paleontology and Evolution, (3rd Edn.)
5. Lindholm,R.C (1987). A practical approach to sedimentology
21-days compulsory field training in the designated field areas. Examination paper for the geology of the field area is required.
- Composition of the Earth and its Relation to the Universe;
- Some thermodynamics and Crystal and Isotopes Chemistry;
- The role of Geochemical Processes in Magmatism, Sedimentation and Metamorphism;
- The Geochemical nature of the Atmosphere, Hydrosphere, and Biosphere;
- Geochemical Cycle
- Introduction to Exploration Geochemistry
Tutorial Work
Tutorial work on crystal and isotopes chemistry, Geochemical processes. Atmosphere, Hydrosphere, and Biosphere. Geochemical cycle, Exploration Geochemistry.
References
Mason, B., (1990), Principles of Geochemistry, (4th Edn.)
- The Oceanic Crust: Structure; Petrology and Sources of Oceanic Crust; Deep-sea drilling data, Evidence from ophiolite complexes, Volcanism at Oceanic Ridges
- Sea-level History and Seismic Stratigraphy
- The Importance of Sea-level Change and its causes
- Quaternary Sea-level History
- Sedimentary Cycles
- Seismic Stratigraphy
- Introduction to Ocean Sediments: Calcareous sediments; Siliceous Sediments; Nature and Distribution of Sediments in Continental Shelf, Slope and Abyssal Plain
- Coastal geology; Marine Sedimentation and Erosional Processes
- Paleooceanography (Deep-sea Records(Ocean Drilling Program)
- Marine Resources and Environmental Concerns
- Placer deposits; Phosphorite, Manganese Nodules; Petroleum and Gas Hydrates
- Environmental Consequences of Marine Mineral Extraction
Tutorial work
Tutorial on Oceanic crust, sea-level history and seismic stratigraphy, coastal geology and oceanic sediments.
References
- Kennet, J. P. (1982) Marine Geology, 2nd Edition, New York, Prentice Hall
- Seibold, E., and Berger, W. H., (1996) The Sea Floor : An Introduction to Marine Geology, Springer-Verlag, 3rd Edition, 356p.
- Duxbury A.C and Duxbury A. B. (1984) An Introduction to World’s Oceans, 2nd Edition
- Erickson. J. (2003) Marine Geology; Exploring the New Frontiers of the Ocean.
- Fundamentals of surveying
- Tape and offset surveying
- Levelling
- The Theodolite and its use
- Electromagnetic distance measurement
- Satellite positioning systems
- Survey Methods
- Orientation and position
- Analysis and adjustment of measurements
- Areas and volumes
- Control and precision
- Hydrographic surveying
Practical Work
Tape and offset surveying, leveling, theodolite, satellite positioning systems, survey methods (Traversing, Triangulation, Total station instruments), orientation and position, Areas and volumes
References
- Davis, R. E., Foote, F., Kelly, J. W. (1966) Surveying, McGraw Hill Book Co., New York.
Bannister, A. and Raymond, S. (1998). Surveying (7th Edition) Longman scientific and Technical, England.
- Introduction; Scope; Historical Development and principles: Uses.
- Geologic Time and Chronology: Development of Geologic Time Scale; Radiometric Dating; Stratigraphic stages.
- Stratigraphic Procedures; Outcrop Procedures; Subsurface Procedures
- Stratigraphic Classification and Nomenclature: Dual classification: Modern classification; Code of stratigraphic nomenclature.
- Sedimentary Facies: Definition; Concepts; Classification; Analysis: Importance.
- Stratigraphic correlation: Principles and problems of lithostratigraphic and chronostratigraphic correlation.
- Stratigraphic maps: Classification; Procedures: Isopach and lithofacies maps uses.
Practical Work / Tutorial
Practical Work / Tutorials on selected lecture and related topics
References
- Krumbein, W.C. & L. L. Sloss, (1963) Stratigraphy and Sedimentation (2nd. ).
- Stokes, W. L. (1966). Essentials of Earth History: an introduction to historical Geology (2nd. ).
- Lemon, R. (1990) Principles of
Doyle, P. & M. R. Bennett (eds) (1999). Unlocking the Stratigraphic Records
- History of geological investigation in Myanmar
- Tectonic provinces and subprovinces
- Neotectonics and earthquakes
- Precambrian Geology
- Lower Paleozoic stratigraphy
- Upper Paleozoic stratigraphy
Practical Work
- Exercises on stratigraphic symbols and chronographic colours
- Systematic study and descriptions of geological maps of selected areas in Myanmar
References
- Chhibber, H. L. (1934) Geology of Burma.
- Bender, F. (1984) The Geology of Burma.
- Win Swe (2012) A briefe outline geology and mineral resources of Myanmar.
4. Maung Thein (2010) Summary of Geological History of Myanmar.
- Brief history of Economic Geology.
- Petrology of mineral deposits: Magmas, solutions and sediments.
- Classification of mineral deposits.
- Processes of formation of mineral deposits (with examples)
- Occurrence of mineral deposits in relation to plate-tectonic settings.
- Mineral Deposits of Myanmar
Practical Work
Laboratory works on ore minerals;
References
- Jeansen, M. L. & A. M. Bateman (1981) Economic Mineral Deposits (3rd Edn.)
- Parks, C. F. & R. A. MacDiarmid (1964) Ore Deposits.
3. United Nations., (1996) Geology and Mineral Resources of Myanmar. Atlas of Mineral Resources of the ESCAP Region V. 12
- Scope and Historical Background.
- Different types of Aerial Photographs; Geometry of Vertical Aerial photographs; Definitions.
- Basic Photogrammetry: scale; relief displacement ; determination of ground co-ordinate; parallax; parallax equation; determination of slope.
- Air-photo Interpretation: identification and interpretative criteria; interpretation of unconsolidated and consolidated materials; structural interpretation; preparation of photogeological maps and stereo-pairs.
- Introduction to Remote Sensing
- Introduction to GIS
Practical Work
Photogeological interpretation of the aerial photographs from some selected areas of Myanmar.
References
- Miller, V. C. & F. Miller (1961). Photogeology.
- Leuder, D. R. (1959) Aerial Photographic Interpretation.
Lillesand, T.M. and R.W. Kiefer (1994) Remote Sensing and Image Interpretation (3rd Edn.)
Engineering Geology
- Application of Geology in field of engineering
- Engineering properties of soil and rock for construction materials
- Site investigation (Dam, Road, Building, Tunnel, Bridge)
- Geological consideration on tunneling
- Environmental consideration on construction of large dam, bridge & tunnel
- Chemical character of ground water
- Ground water exploration
Tutorial / Practical Work
- Exercises on engineering geological problems
HydroGeology
- Hydrologic cycle and individual hydrological processes
- Origin and occurrence of groundwater
- Geologic formation as aquifers
- Rocks properties affecting groundwater
- Groundwater movement
- Chemical characteristics of groundwater
- Groundwater exploration
Tutorial / Practical Work
- Exercises on hydrologic problems
References
- Krynine, P. P., and W. R. Judd (1957) Engineering Geology and Geotechnics.
- Ringers, R. (1981) Principles of Engineering Geology. ITC Handbook, Enschede.
- Davis, S.N., and R. J. M. Dewest (1967) Hydrogeology.
- G.Driscoll (1986) Ground water and wells (2nd Ed).
- L. Jat and S. R. Bhaker (2009) Groundwater Hydrology
David Keith Todd (2005) Groundwater Hydrology (3rd Ed).
- Definition and scope
- Stratigraphic chart
- Beginning of life and Precambrian Fossils;
- Historical Geology of Paleozoic Era;
- Historical Geology of Mesozoic Era;
- Historical Geology of Tertiary Period;
- Historical Geology of Quaternary Period;
Tutorial
Tutorial on selected lecture and relative topics
References
- Stokes, W. L. (1966) Essentials of Earth History: an introduction to historical geology (2nd Edn.)
2. Dunbar, C. O. (1963) Historical Geology (2nd Edn.).
- Frequency distribution: Histograms and Frequency polygon; Relative frequency distribution; Cumulative frequency distribution
- Analysis of variance
- Correlation and regression; Dendrograms
- The Chi-Square Test
- Markov Chain Analysis
Tutorial
Tutorial on selected lecture and related topics
References
Spiegel, M. R. (1961) Geostatistics, Schaum’s Outline Series
- Mineral belts and mineral epochs of Myanmar
- Tin-tungsten deposits
- Lead-zinc-silver deposits
- Nickel-chromium deposits
- Copper deposits
- Antimony deposits
- Iron deposits
- Gold deposits
- Gemstone deposits
- Major oil and gas fields
- Coal deposits
Practical Work / Tutorial
Tutorial on selected lecture and related topics
References
- Clegg, E.L.G., (1944) Mineral Deposits of Burma.
- Bender, F., (1983). Geology of Burma.
- United Nations., (1996) Geology and Mineral Resources of Myanmar. Atlas of Mineral Resources of the ESCAP Region V. 12
4. Win Swe (2012). A brief outline Geology and Mineral Resources of Myanmar.
- Mesozoic stratigraphy
- Tertiary stratigraphy
- Quaternary stratigraphy
- Geological evolution of Myanmar
Practical Work
Systematic study and descriptions of geological maps of selected areas in Myanmar
References
- Chhibber, H. L. (1934) Geology of Burma.
- Bender, F. (1984) Geology of Burma.
- Mg Thein (2010) Summary of Geological History of Myanmar.
- De Terra, H, (1943) Pleistocene of Burma.
- Chit Saing (1998) Mesozoic and Tertiary Stratigraphy of Myanmar.
6. Win Swe (2012). A brief outline Geology and Mineral Resources of Myanmar.
- Exploration Sequences; Methods and techniques in mineral exploration; Exploration Stages; Exploration Ore Guides
- Geological prospecting and exploration
- Geochemical prospecting and exploration
- Geophysical prospecting and exploration
Practical Work
Exercises on the uses, calculations and interpretations of geological, geochemical, and geophysical data and information
References
- Peter, W. ((1985). Exploration and Mining Geology
- Rose, A., H.E. Hawkes and J.S.Webb (1984) Geochemistry in mineral exploration.
Parasnis (1986). Principles of Applied Geophysics (4th.Ed.)
21-days compulsory field training designated field area.
Examination for the geology of the assigned area is required.
-
- The Scope of Petroleum Geology
- Physical and Chemical Properties of Petroleum
- Methods of Exploration
- Transformation of hydrocarbons (Petroleum systems): Origin; Migration; Petroleum accumulation
- Production Methods
- Traps and Seals: Seal and Cap; Classification and type of Trap; Stratigraphy of the basin;
- Reservoirs: Porosity and Permeability; Reservoir Correlations; Reserve calculation
Practical Work /Tutorial
Tutorial on selected lecturers and related topics
References:
R. C. Selley (1998) Elements of Petroleum Geology, 2nd Edition
- Physical and optical properties of gem materials
- Theory and use of instruments used in gem-testing
- Various methods used in gem identification
- Enhancement of gemstones
- Description of gemstones (with emphasis on precious stones)
Practical Work
- Hand specimen identification
- Identification of individual gemstones using various methods
References
Hurlbut, Jr., C.S. and R.C. Kammerling (1991) Gemmology. (2nd Edn.).
-
- Definition; Scope and Concept of Quaternary Geology
- Glacial and Interglacial periods; Pluvial and Interpluvial periods
- European and American Stages
- Paleoclimatic Phenomena
- Sea-level Fluctuation
- Quaternary Deposits
- Dating for Quaternary Sediments
Tutorial
Tutorial on selected lecture and related topics
References
- Flint R.F (1971). Glacial and Quaternary geology.
Embleton, C and C. A M King, (1969). Glacial and Periglacial morphology.
- Introduction
- Magmatic processes: stages in magmatic consolidation: fractional crystallization and Bowen’ reaction series
- Igneous structures and field relationships
- Textures and microstructures of igneous rocks
- IUGS Classification of Igneous rocks
Practical Work
- Megascopic petrography of igneous rocks of Myanmar.
- Textures and microstructures of igneous rocks in thin section.
References
- Williams, H, F. J. Turner & C. M. Gilbert (1954). Petrography.
- Hatch, F. H., A.K. Wells & M. K. Wells (1972). Petrology of the Igneous Rocks (3rd. Edn.).
- Hyndman, D. W., (1985) Petrology of igneous and metamorphic rocks (2nd Ed.)
4. Winter, J. D. (2001). An Introduction to Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology.
- Introduction; Scope; History; Uses
- Processes of sedimentation; Weathering; Erosion; Transportation; Deposition and Depositional Environments; Post-depositional Changes.
- Properties of sediments: Textures; Structures; Composition; Mass properties
- Products of sedimentation; Classification of sedimentary rocks
Practical Work
- Megascopic petrography of common sedimentary rocks
- Size frequency distribution
- Microscopic study of clastic sedimentary rocks
References
- Pettijohn, F. J. (1975). Sedimentary Rocks. (3rd. Edn.)
- Williams, H., F.J. Turner & C.M. Gilbert (1954). Petrography
- Reineck, H. E. and I. B. Singh (1980) Depositional Sedimentary Environment with reference to Terrigeneous clastics, (Second Revised and Update Edition)
- Blatt, H., G. Middleton, R. Murray (1980) Origin of Sedimentary Rocks, 2nd Edition.
5. Tucker, H. E, (1991) Sedimentary Petrology (2nd Ed.)
- Introduction, meaning and scope.
- Fossils and fossilization.
- Systematic and nomenclature
- Systematic study of phyla Protozoa, Porifera, Coelenterata, Bryozoa, Graptolithina, mentioning general features, morphological characteristics, classification, paleoecology, and stratigraphic significance.
Practical Work
- Types of fossilization
- Identification and systematic description of selected important genera of phyla Protozoa, Porifera, Coelenterata, Bryozoa and Graptolithina.
References
- Shrock , R. R., & W. H. Twenhofel (1953) Principles of Invertebrate Paleontology
- Moore, R. C., C. G. Lalicker & A. G. Fischer, (1952) Invertebrate Fossils
- Easton, W. H. (1960) Invertebrate Paleontology
4. Clarkson, E. N. K. (1993) Invertebrate Paleontology and Evolution (3rd Ed.)
T
- Introduction: Scope; History
- Metamorphism: Agents; Processes; Types
- Textures and structures of metamorphic rocks
- Classification of metamorphic rocks
- Metamorphic grades, zones and facies
- Metamorphism of politic, quartzzo-feldspathic, calcareous, magnesian, and basic rocks
- Relationship between regional metamorphism and tectonism
- Metamorphic belts and Epochs of Myanmar
Practical works
- Megascopic petrology of common metamorphic rocks
- Textures of metamorphic rocks
- Microscopic petrology of common metamorphic rocks
References
- Williams, H, F. J. Turner & C. M. Gilbert (1954). Petrography.
- Winter, J. D. (2001) An Introduction to Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology
- Hyndman, D. W., (1985) Petrology of Igneous and Metamorphic Rocks, New York, McGraw Hill, 2nd edition.
- Raymond, L. A (1995). Petrology (igneous, sedimentary, metamorphic rocks)
5. Yardley, B.W. D (1983), An introduction to metamorphic petrology
- Introduction to Geophysics: Physical properties of Rocks and Minerals; Classification of Geophysical Methods; The Geophysical Model; Direct and Indirect Application; Ambiguity in Interpretation.
- The basic principles and practices in Gravity Method: Magnetic method, Electrical method, Resistivity method, Electromagnetic method, Induced polarization method, Radioactive method and seismic method.
Tutorial / Practical Work
- Tutorial on Subfields of Geophysics; Petrophysical properties; Principles of Geophysics; Geophysical methods
References
- Parasnis (1986). Principles of Applied Geophysics, 4th edition.
2. Howell, A. K. : Introduction to Geophysics
- Overview and History of Marine Geology; Internal Structures of the Earth; The earth’s gravity field; The earth’s magnetic field
- Geophysics and Ocean Morphology; The Continental Margin; The Oceanic Ridges; Fracture Zones; The Ocean-Basin Floor; Marginal Trenches; Seismic Reflection; Seismic Refraction
- Ocean Basin Tectonics: Principal Features of Ocean Spreading Centres; Principal Features of Ocean Subduction Zones
- Study of Continental Margins; Passive Continental Margins (Rift Phenomena); Active Continental Margins (Accretionary Prisms)
- Submarine and island arc volcanoes.
Tutorial Work
Ocean morphology, ocean basin tectonics, continental margins
References
- Kennet, J. P. (1982) Marine Geology, 2nd Edition, New York, Prentice Hall
- Seibold, E., and Berger, W. H., (1996) The Sea Floor : An Introduction to Marine Geology, Springer-Verlag, 3rd Edition, 356p.
- Duxbury A. C. and A. B. Duxbury (1984) An Introduction to World’s Oceans, 2nd Edition.
- Erickson.J. (2003). Marine geology; Exploring the News frontiers of the ocean.
- Basic concepts of geomorphology; Scale, processes, structural influences, climate, people as geomorphic agents.
- Fluvial processes and their landforms; Streams and valleys; Drainage patterns; Stream meandering; Fluvial cycles; River terraces; Peneplain concept.
- Tectonic and structural landforms; Landforms controlled by faults; Landforms controlled by folds.
- Karst landforms: Surface landforms; Subsurface caves and springs; Karst evolution.
- Coastal processes and landforms: Tides, waves and currents: Eustatic sea-level changes; Erosional and depositional landforms of coasts; deltas and estuaries; Continental shelves and submarine canyons.
- Paleogeomorphology: Relict landforms; Burried landforms; Exhumed landforms.
- Applied geomorphology: Application to Hydrology; Application to economic geology; Application to Engineering projects; Application to oil exploration.
Practical Work
- Interpretation of topographic maps for the purpose of geologic information.
- Interpretation of air-photographs and geological maps.
References
- Thornbury, W.D. (1969). Principles of Geomorphology. (2nd Edn.)
- Selby, M.J. (1985). Earth’s Changing Surface; An Introduction to Geomorphology.
- Petrography of various clans of the acid, intermediate, basic and ultrabasic groups, pyroclastic rocks and lamprophyres
- Igneous associations at various plate boundaries
- A brief account of igneous activity of Myanmar
- Brief account of the major granitoid belts of Myanmar
- The Central Igneous Belt
Practical Work
Microscopic petrography of igneous rocks of Myanmar.
References
- Williams, H, F. J. Turner & C. M. Gilbert (1954). Petrography.
- Hatch, F. H., A.K. Wells & M. K. Wells (1972). Petrology of the Igneous Rocks (3rd Edn.)
3. Winter, J. D. (2001). An Introduction to Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology
- Clastic sedimentary rocks: Conglomerates and breccias; Sandstones; Siltstones; Shales.
- Chemical and organic sedimentary rocks: Limestones; Dolomites and dolomitization; Chert; Evaporites; Iron formations
- Depositional environments and facies of alluvial, deltaic, shallow marine (with tempestite and tsunamites), deep sea and pelagic sedimentation.
Practical Work
- Megascopic petrography of common sedimentary rocks of alluvial, deltaic, shallow marine (with tempestite and tsunamites), deep sea and pelagic sedimentation.
- Microscopic petrography of sandstones and limestones
References
- Pettijohn, F. J. (1975). Sedimentary Rocks. (3rd. Edn.)
- Williams, H., F.J. Turner & C.M. Gilbert (1954) Petrography
- Reineck, H. E. and I. B. Singh (1980) Depositional Sedimentary Environment with reference to Terrigeneous clastics, (Second Revised and Update Edition)
- Blatt, H., G. Middleton, R. Murray (1980) Origin of Sedimentary Rocks, 2nd Edition.
5. Tucker, H. E. (1991) Sedimentary Petrology. 2nd Edition.
- Systematic study of phyla Echinodermata, Arthropoda, Brachiopoda, and Mollusca, mentioning general features, morphological characteristics, classification, paleoecology, and stratigraphic importance.
- Introduction to trace fossils.
Practical Work
Study of morphological features, identification and systematic description of selected important genera of phyla Echinodermata, Arthropoda, Brachiopoda and Mollusca and trace fossils.
References
- Shrock, R. R., & W. H. Twenhofel (1953) Principles of Invertebrate Paleontology
- Moore, R. C., C. G. Lalicker & A. G. Fischer, (1952). Invertebrate Fossils
- Easton, W. H. (1960). Invertebrate Paleontology
- Clarkson, E. N. K. (1993). Invertebrate Paleontology and Evolution, (3rd Edn.)
5. Lindholm,R.C (1987). A practical approach to sedimentology
21-days compulsory field training in the designated field areas. Examination paper for the geology of the field area is required.
- Composition of the Earth and its Relation to the Universe;
- Some thermodynamics and Crystal and Isotopes Chemistry;
- The role of Geochemical Processes in Magmatism, Sedimentation and Metamorphism;
- The Geochemical nature of the Atmosphere, Hydrosphere, and Biosphere;
- Geochemical Cycle
- Introduction to Exploration Geochemistry
Tutorial Work
Tutorial work on crystal and isotopes chemistry, Geochemical processes. Atmosphere, Hydrosphere, and Biosphere. Geochemical cycle, Exploration Geochemistry.
References
Mason, B., (1990), Principles of Geochemistry, (4th Edn.)
- The Oceanic Crust: Structure; Petrology and Sources of Oceanic Crust; Deep-sea drilling data, Evidence from ophiolite complexes, Volcanism at Oceanic Ridges
- Sea-level History and Seismic Stratigraphy
- The Importance of Sea-level Change and its causes
- Quaternary Sea-level History
- Sedimentary Cycles
- Seismic Stratigraphy
- Introduction to Ocean Sediments: Calcareous sediments; Siliceous Sediments; Nature and Distribution of Sediments in Continental Shelf, Slope and Abyssal Plain
- Coastal geology; Marine Sedimentation and Erosional Processes
- Paleooceanography (Deep-sea Records(Ocean Drilling Program)
- Marine Resources and Environmental Concerns
- Placer deposits; Phosphorite, Manganese Nodules; Petroleum and Gas Hydrates
- Environmental Consequences of Marine Mineral Extraction
Tutorial work
Tutorial on Oceanic crust, sea-level history and seismic stratigraphy, coastal geology and oceanic sediments.
References
- Kennet, J. P. (1982) Marine Geology, 2nd Edition, New York, Prentice Hall
- Seibold, E., and Berger, W. H., (1996) The Sea Floor : An Introduction to Marine Geology, Springer-Verlag, 3rd Edition,.
- Duxbury and Alison B. Duxbury (1984) An Introduction to World’s Oceans, 2nd Edition
4. Erickson. J. (2003) Marine Geology; Exploring the New Frontiers of the Ocean.
- Fundamentals of surveying
- Tape and offset surveying
- Levelling
- The Theodolite and its use
- Electromagnetic distance measurement
- Satellite positioning systems
- Survey Methods
- Orientation and position
- Analysis and adjustment of measurements
- Areas and volumes
- Control and precision
- Hydrographic surveying
Practical Work
- Tape and offset surveying, leveling, theodolite, satellite positioning systems, survey methods, (Traversing, Triangulation, Total station instrument). Orientation and position, Area and volumes.
References
- Davis, R. E., Foote, F., Kelly, J. W. (1966) Surveying, McGraw Hill Book Co., New York.
Bannister, A. and Raymond, S. (1998). Surveying (7th Edition) Longman scientific and Technical, England.
- Introduction; Scope; Historical Development and principles: Uses.
- Geologic Time and Chronology: Development of Geologic Time Scale; Radiometric Dating; Stratigraphic stages.
- Stratigraphic Procedures; Outcrop Procedures; Subsurface Procedures
- Stratigraphic Classification and Nomenclature: Dual classification: Modern classification; Code of stratigraphic nomenclature.
- Sedimentary Facies: Definition; Concepts; Classification; Analysis: Importance.
- Stratigraphic correlation: Principles and problems of lithostratigraphic and chronostratigraphic correlation.
- Stratigraphic maps: Classification; Procedures: Isopach and lithofacies maps uses.
Practical Work / Tutorial
Tutorials on selected lecture and related topics
References
- Krumbein, W.C. & L. L. Sloss, (1963) Stratigraphy and Sedimentation (2nd. ).
- Stokes, W. L. (1966). Essentials of Earth History: an introduction to historical Geology (2nd. ).
- Lemon, R. (1990) Principles of
Doyle, P. & M. R. Bennett (eds) (1999). Unlocking the Stratigraphic Records
- History of geological investigation in Myanmar
- Tectonic provinces and subprovinces
- Neotectonics and earthquakes
- Precambrian geology
- Lower Paleozoic stratigraphy
- Upper Paleozoic stratigraphy
Practical Work
- Exercises on stratigraphic symbols and chronographic colours
- Systematic study and descriptions of geological maps of selected areas in Myanmar
References
- Chhibber, H. L. (1934) Geology of Burma.
- Bender, F. (1984) The Geology of Burma.
- Win Swe (2012) A briefe outline geology and mineral resources of Myanmar.
4. Maung Thein (2010) Summary of Geological History of Myanmar.
- Brief history of Economic Geology.
- Petrology of mineral deposits: Magmas, solutions and sediments.
- Classification of mineral deposits.
- Processes of formation of mineral deposits (with examples)
- Occurrence of mineral deposits in relation to plate-tectonic settings.
- Mineral Deposits of Myanmar
Practical Work
Practical on ore minerals
References
- Jeansen, M. L. & A. M. Bateman (1981) Economic Mineral Deposits (3rd Edn.)
- Parks, C. F. & R. A. MacDiarmid (1964) Ore Deposits.
- Scope and Historical Background.
- Different types of Aerial Photographs; Geometry of Vertical Aerial photographs; Definitions.
- Basic Photogrammetry: scale; relief displacement ; determination of ground co-ordinate; parallax; parallax equation; determination of slope.
- Air-photo Interpretation: identification and interpretative criteria; interpretation of unconsolidated and consolidated materials; structural interpretation; preparation of photogeological maps and stereo-pairs.
- Introduction to Remote Sensing
- Introduction to GIS (Geographic information system)
Practical Work
Photogeological interpretation of the aerial photographs from some selected areas of Myanmar.
References
- Miller, V. C. & F. Miller (1961). Photogeology.
- Leuder, D. R. (1959) Aerial Photographic Interpretation.
- Lillesand, T.M. and R.W. Kiefer (1994) Remote Sensing and Image Interpretation (3rd Edn.)
Engineering Geology
- Application of Geology in field of engineering
- Engineering properties of soil and rock for construction materials
- Site investigation (Dam, Road, Building, Tunnel, Bridge)
- Geological consideration on tunneling
- Environmental consideration on construction of large dam, bridge & tunnel
- Chemical character of ground water
Ground water exploration
Tutorial / Practical Work
- Exercises on engineering geological problems
Hydrogeology
- Hydrologic cycle and individual hydrological processes
- Origin and occurrence of groundwater
- Geologic formation of aquifers
- Rock properties affecting groundwater
- Groundwater movement
- Chemical characters of groundwater
- Groundwater exploration
Tutorial /Practical Work
- Exercises on hydrogeologic problems
References
- Krynine, P. P., and W. R. Judd (1957) Engineering Geology and Geotechnics.
- Ringers, R. (1981) Principles of Engineering Geology. ITC Handbook, Enschede.
- Davis, S.N., and R. J. M. Dewest (1967) Hydrogeology.
- Fletcher.G.Driscoll (1986) Ground water and wells (2nd Ed).
- M. L. Jat and S. R. Bhaker (2009) Groundwater Hydrology
- David Keith Todd (2005) Groundwater Hydrology (3rd Ed).
- Definition and scope
- Stratigraphic chart
- Beginning of life and Precambrian Fossils;
- Historical Geology of Paleozoic Era;
- Historical Geology of Mesozoic Era;
- Historical Geology of Tertiary Period;
- Historical Geology of Quaternary Period;
Tutorial
Tutorial on selected lecture and relative topics
References
- Stokes, W. L. (1966) Essentials of Earth History: an introduction to historical geology (2nd Edn.)
2. Dunbar, C. O. (1963) Historical Geology (2nd Edn.).
- Histograms and Frequency polygon; Relative frequency distribution; Cumulative frequency distribution
- Analysis of variance
- Correlation and regression; Dendrograms
- The Chi-Square Test
- Markov Chain Analysis
Tutorial
Tutorial on selected lecture and related topics
References
Spiegel, M. R. (1961) Geostatistics, Schaum’s Outline Series
- Mineral belts and mineral epochs of Myanmar
- Tin-tungsten deposits
- Lead-zinc-silver deposits
- Nickel-chromium deposits
- Copper deposits
- Antimony deposits
- Iron deposits
- Gold deposits
- Gemstone deposits
- Major oil and gas fields
- Coal deposits
Practical Work / Tutorial
Tutorial on selected lecture and related topics
References
- Clegg, E.L.G., (1944) Mineral Deposits of Burma
- Bender, F., (1983). Geology of Burma
- United Nations., (1996) Geology and Mineral Resources of Myanmar. Atlas of Mineral Resources of the ESCAP Region V. 12
4. Win Swe (2012). A brief outline Geology and Mineral Resources of Myanmar.
- Mesozoic stratigraphy
- Tertiary stratigraphy
- Quaternary stratigraphy
- Geological evolution of Myanmar
Practical Work
Systematic study and descriptions of geological maps of selected areas in Myanmar
References
- Chhibber, H. L. (1934) Geology of Burma.
- Bender, F. (1984) Geology of Burma.
- Mg Thein (2010) Summary of Geological History of Myanmar.
- De Terra, H, (1943) Pleistocene of Burma.
- Chit Saing (1998) Mesozoic and Tertiary Stratigraphy of Myanmar.
6. Win Swe (2012). A brief outline Geology and Mineral Resources of Myanmar.
- Exploration Sequences; Methods and techniques in mineral exploration; Exploration Stages; Exploration Ore Guides
- Geological prospecting and exploration
- Geochemical prospecting and exploration
- Geophysical prospecting and exploration
Practical Work
Exercises on the uses, calculations and interpretations of geological, geochemical, and geophysical data and information
References
- Peter, W. (1985). Exploration and Mining Geology
- Rose, A., H.E. Hawkes and J.S.Webb (1984) Geochemistry in mineral exploration.
Parasnis (1986). Principles of Applied Geophysics (4th.Ed.)
21-days compulsory field training designated field area.
Examination for the geology of the assigned area is required.
- The Scope of Petroleum Geology
- Physical and Chemical Properties of Petroleum
- Methods of Exploration
- Transformation of hydrocarbons (Petroleum systems): Origin; Migration; Petroleum accumulation
- Production Methods
Traps and Seals: Seal and Cap; Classification and type of Trap; Stratigraphy of the basin;
- Reservoirs: Porosity and Permeability; Reservoir Correlations; Reserve calculation
Tutorial Work:
Tutorial on selected lecturers and related topics
References:
R. C. Selley (1998) Elements of Petroleum Geology, 2nd Edition
- Physical and optical properties of gem materials
- Theory and use of instruments used in gem-testing
- Various methods used in gem identification
- Enhancement of gemstones
- Description of gemstones (with emphasis on precious stones)
Practical Work
- Hand specimen identification
- Identification of individual gemstones using various methods
References
Hurlbut, Jr., C.S. and R.C. Kammerling (1991) Gemmology. (2nd Edn.).
Error Analysis
- Definition; Scope and Concept of Quaternary Geology
- Glacial and Interglacial periods; Pluvial and Interpluvial periods
- European and American Stages
- Paleoclimatic Phenomena
- Sea-level Fluctuation
- Quaternary Deposits
- Dating for Quaternary Sediments
Tutorial
Tutorial on selected lecture and related topics
References
- Flint R.F (1971). Glacial and Quaternary geology.
Embleton, C and C. A M King, (1969). Glacial and Periglacial morphology.
- Review of optical properties of minerals under the orthoscope
- Optical properties of minerals under the conoscope
- Uniaxial Minerals Wave-velocity surfaces, optical indicatrix, interference figures, optic sign
- Biaxial Minerals: Wave velocity surface, optical indicatrix, interference figures, optic sign, and optic angle.
- Interference colours in relation to thickness and optical orientation; Uses of colour chart.
- Optical orientation of biaxial minerals; Construction of orientation diagrams.
Practical Work
- Orthoscope and conoscope
- Uniaxial minerals under the conoscope: interference figures, determination of optic sign.
- Biaxial minerals under the conoscope: interference figures, determination of optic sign and optic angle.
- Exercise on optical orientation diagrams.
References
- Kerr, P.F.(1977). Optical Mineralogy. (4th).
- Wahlstrom, E.E (1969). Optical Crystallography. (4th Ed.).
Igneous Petrology
- Modern classification of igneous rocks
- Heterogenous equilibria (Phase diagrams and magmatic crystallization)
- Petrographic modal analysis
- Norms and Norm Calucation
- Genetic types of granite
- Granitoid Rocks of Myanmar
- Ophiolite Belts of Myanmar
Metamorphic Petrology
- Review on metamorphic facies
- Metamorphic facies and facies series
- Plate tectonics and metamorphism
- Some examples of metamorphic regions in Myanmar
– Mogok Metamorphic Belt
– Shantaung U-Thandawmyat Range
Practical Work
- Modal analysis by point counting
- Norm calucation
- Exercises on lithologic associations
- Microscopic petrography of selected igneous and metamorphic rocks from Myanmar
References
- Hyndman, D.W. (1985). Petrology of Igneous and Metamorphic Rocks. (2nd).
- Winkler H.G.F (1979), Petrogenesis of Metamorphic Rocks.
- Historical background; Means of obtaining remote-sensing information.
- Basic principles: Spectrum and spectral characteristics; Passive and active remove sensing
- Sensors and Sensor platforms
- The Landsat system; Application and results
- Spectral signatures of the terrain objects
- Spectral analysis of the terrain objects from black-and-white images and false-colour images
- Remote-sensing application in mineral exploration
- Analysis of Geological structures from satellite images
- Geographic Information System: Basic principles and procedures
Practical Work
- Interpretation of satellite images and preparation of Geological maps
- Exercises on G.I.S
References
- Lillesand, T.M. and R.W. Kiefer (1994). Remote Sensing and image Interpretation (3rd).
- Barett, E.C and L.F Curtis (1976) Introduction to Environmental Remote Sensing
- New developments in plate-tectonic theory
- Types of continental margins
- Concept of accreted terranes
- Plates tectonics and mineralization
- A brief account of tectonics of Southeast Asia
- Geodynamics of India-Asia Collision
Tutorial Work
Tutorials on selected lecture and related topics
References
- Cox, A. and R.B. Hart, (1986). Plate Tectonics: How It Works
- Shia, J.H. (Ed.) (1985). Plate Tectonics.
- Hutchison, C.S. (1989). Geological Evolution of Southeast Asia.
GIAC (1999). Report on Geodynamics of India-Asia Collision
Research Methodology I
- Basic concepts and Approaches
- Data collection and Analysis
Project Assignment
Project assignment for each student to write papers on the assigned topics in the following fields of study: Mineralogy, Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology, Sedimentology, Paleontology, Structural Geology, Economic Geology, Myanmar Geology. Seminar presentations and examination for the papers submitted are required.
References
Myanmar Academy of Art and Science (2002). Research Method in Art and Science.
- Regional stratigraphy of South India and the Himalayas.
- Regional stratigraphy of Thailand
- Regional stratigraphy of Yunnan
- Tertiary stratigraphy of Assam and Indonesia
Practical \ Tutorial Work
Systematic study and descriptions of selected Geological maps from the neighboring countries\ Tutorials on selected lecture and related topics
References
- Wadia, D.N. (1966). Geology of India
- Hutchison; C.S. (1989). Geological Evolution of Southeast Asia (2nd Ed.)
- Vertebrate Paleontology
- Definition; Evolution of the vertebrates; Lower vertebrates (Ostracoderms); Fishes (Chondrichthyes, Ostichthyes); Amphibians;
- Reptiles; Mammals; Primates (Lower primates, Higher primates); Evolution of Man
Micropaleontology
- Scope and definition; Brief accounts on various groups of microfossils
- The Study of Foraminifers: Morphology and structures of foraminifers; Ecology and paleoecology; Stratigraphic distribution and economic uses;
- Systematic study of some important foraminifera groups.
Practical Work
- Systematic study of important vertebrate fossil groups
- Systematic study of important microfossil groups
References:
- Romer, A.S. (1966). Vertebrate Paleontology (3rd)
- Glaessner, M.F. (1947). Principles of Micropaleontology
- Moore, R.C.C.G. Lalicker & A.G. Fischer, (1952). Invertebrate Fossils
- Clarkson, E.N.K. (1993). Invertebrate Paleontology and Evolution (3rd)
- Robert, L. Carroll (1988). Vertebrate Paleontology and Evolution.
- Fleagle, J.G. (1999). Primate Adaptation and Evolution.
- Neild, E. W and Tucker, B. C. T. (1992). Paleontology: An Introduction.
- Sedimentology
- Common sedimentary environments and facies (Both clastics and Carbonates)
- Clastic rocks: Petrography and origin of principal sandstone type
- Sandstone composition, provenavces and tectonic setting
- Carbonate rocks: Petrography
- Clay minerals
- Mud rocks
Practical Work
Microscopic study of clastic and carbonate rocks
Mechanical analysis of clastic rocks
References
- Pettijohn, F.J. (1975).Sedimentary Rocks (3rd)
- Williams, H,F.J. Turner & C.M. Gibert (1954).Petrolography
- Reineck, H.E. and I .B. Singh (1980) Depositional Sedimentary Environment with References to Terrigeneous clastics, (Second Revised and Update Edition)
- Balatt, H., G. Middleton, R. Murray (1880) Origin of Sedimentary Rocks (2nd)
- Tucker, H. E. (1991) Sedimentary Facies in Geologic History.
- Wilson (1975) Carbonate Facies in Geologic History.
-
- Resource and reserve: classification of reserves by U. S. G. S and Ministry of Mines, Myanmar.
- Drilling in minaeral exploration: types of drills, Geologist’s responsibilities.
- Sampling and ore reserve estimation: sampling techniques: methods of ore reserve estimation.
- Definitions of mining terms
- Introduction to mining methods.
- Basic principles of minearal dressing.
Practical Works and Tutorials
- Averaging assays.
- Ore reserve calculation.
- Tutorials on selected lecture and related topics
References
- Peters, W .C. (1985). Exploration and Mining Geology
- Rose, A., H. E. Hawkes and J. S Webb (1984). Geochemistry in mineral exploration.
- McKinstry, H. (1960). Mining Geology.
-
- Gemmology
- Definition of Gem Minerals
- Physical and Optical Properties of Gem Minerals
- Principles and Applications of Gem Testing Instruments
- Gem Testing Methods
- Description and Identification of Gemstones (Precious and Assorted Gems)
Practical Work
- Identification of rough gemstones with hand lens
- Identification of gemstones with gem testing instruments
References
- Hurlbut, Jr., C.S and Kammaerling , R.C. (1991) Gemmology. (2nd)
Seismology
- History of seismology
- Earthquake geography and plate tectonics
- Causes of earthquakes: earthquake sources
- Seismic waves
- Measuring earthquakes: epicenter and magnitudes
- Seismic gap hypothesis
- Prediction of earthquakes
- Review of earthquake hazards in Myanmar
- Migration of hazards in Myanmar
- Introduction to earthquake engineering
Practical Work/ Tutorial
- Determination of earthquake epicenter and magnitude
- Exercises of seismic zoning
- Tutorials on selected lecture and related topics
References
- Bolts, B. A. (1993) , Earthquakes
- Yeats, Rl. S., Seih, Kand Allen, C. R. (1997). The Geology of Earthqukes.
- Kramer, S. L. (1996). Geotechnical Earthquake Engineering.
- Maung Thein (2011). Earthquakes in Myanmar, Vol. 1& 2.
- Gemmology
-
- Research Methodology IIMethods for Geologic Mapping, Petrologic, Stratigraphic and Paleontologic Research.
Project Assignment
Project assignments for each student to write papers on the assigned topics in the following fields of study: Mineralogy, Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology, Sedimentary,Paleontology, structural Geology, Economic Geology, Myanmar Geology. Seminar presentation and examination for the papers submitted are required.
- Research Methodology IIMethods for Geologic Mapping, Petrologic, Stratigraphic and Paleontologic Research.
-
- 30-day compulsory field training in the designated field areas. Examination paper for the Geology of the field area is required.
Geomorphology with special reference to air-photo interpretation; Techniques of air-photo interpretation in geology; Air-photo interpretation of depositional landforms; Structural interpretation of air-photos; Sensor principles and capabilities, specific properties of images and records. Remote-sensing in geologic mapping; Remote sensing in Applied Geology; Remote sensing as an aid in development and the evaluation of natural hazards. Type of images and image processing methods.
Micropaleontology; Ichnology; Conodonts
Current trends in structural geology; Stress and strain in two dimensions; Behaviour of rock deformation; Rock behavior under experimental conditions; Dynamics of faulting; Analysis of macro-structures; Petrofabrics; Morphotectonics.
Petrographic methods- a review; Modern classification and nomenclature of hard rocks; Genetic types of granitoids; Granitoid rocks of Myanmar; Metamorphic facies and facies series- a review; Metamorphic Epochs and Metamorphic Belts of Myanmar; Geochemical Cycles.
Overview and general consideration; Nature and aspects of various geologic hazards:-hazards from earthquakes, hazards from volcanic eruption, hazards from ground failures, ways and means of mitigating these hazards; Earthquake prediction and control; Proper use and care for Earth resources:-groundwater resources, mineral resources, fossil fuel, soil; Geologic condition for proper waste disposal; Use of environmental potential maps in regional planning; Disaster Management and Risk Reduction.
Recent advances in plate tectonics; Magmatism, metamorphism, sedimentation and metallogeny along different plate boundaries; Origin of marginal basins; Collision tectonics of India and Eurasia; Geodynamics of South-east Asia.
Introduction and general consideration; Principles and problems of classification of sedimentary rocks; Clay minerals; Mud rocks; Turbidites, Flysch; Molasses; Sedimentation as ore genesis; Applied sedimentation.
Sedimentary environments and facies: – alluvial, deltaic, estuarine, clastic shoreline, carbonate platform, bathyal, abyssal, trench; Carbonate petrography; Carbonate microfacies analysis; Organism and sediments; Phosphate; Bedded chert.
Stratigraphic invertebrate paleontology of the Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and Cenozoic rock sequences; Sedimentologic and stratigraphic application of selected groups of the invertebrates and microfossils; Depo-environments.
(OR)
Geology of the Moon; Mineral belts and mineral epochs of Myanmar; Mineralization at spreading centers; Quaternary stratigraphy of South-East Asia; Theory of evolution- a critical review; and other current topics.
Geol 632R RESEARCH PROGRESS AND SEMINARS
Geol 641R RESEARCH OUTCOMES AND SEMINARS
Geol 642R THESIS AND VIVA VOCE
Abundance and geochemical classification of elements; Radioactivity and geochronology; Thermodynamics; Crystallization in igneous rocks melts.
Micropaleontology; Ichnology; Conodonts
(OR)
Orthoscopic and conoscopic studies of minerals; Review of silicate structure; Isomorphism and polymorphism in minerals; Solid solution in mineral groups; Systematic microscopic study of all important rock-forming mineral groups with emphasis on feldspar, pyroxene, micas ,aluminosilicates and garnets.
Current trends in structural geology; Stress and strain in two dimensions; Behaviour of rock deformation; Rock behavior under experimental conditions; Dynamics of faulting; Analysis of macro-structures; Petrofabrics; Morphotectonics.
Petrographic methods- a review; Modern classification and nomenclature of hard rocks; Genetic types of granitoids; Granitoid rocks of Myanmar; Metamorphic facies and facies series- a review; Metamorphic Epochs and Metamorphic Belts of Myanmar; Geochemical Cycles.
Element association in igneous rocks and minerals. Geochemistry of metamorphic processes; Sedimentary geochemistry;The hydrosphere; Atmosphere.
Historical development of petrology; Petrogenetic models; Experimental petrology and its uses; Origin of granitic and basaltic magmas; Magma association in relation to plate tectonic settings; Carbonatites; Metamorphism in relation to plate convergence.
Introduction and general consideration; Principles and problems of classification of sedimentary rocks; Clay minerals; Mud rocks; Turbidites, Flysch; Molasses; Sedimentation as ore genesis; Applied sedimentation.
Sedimentary environments and facies: – alluvial, deltaic, estuarine, clastic shoreline, carbonate platform, bathyal, abyssal, trench; Carbonate petrography; Carbonate microfacies analysis; Organism and sediments; Phosphate; Bedded chert.
Stratigraphic invertebrate paleontology of the Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and Cenozoic rock sequences; Sedimentologic and stratigraphic application of selected groups of the invertebrates and microfossils; Depo-environments.
(OR)
Scanning Electron Microscope:- General principles of Electron Microscopy; Image formation and electron diffraction; Sample preparation; Scattering of electrons by crystalline solids; Electron optical contrast phenomena. Electron Probe Micro-Analysis:- Instrumentation; The x-ray detection system; Sample preparation; Qualitative and quantitative analyses; Standards and calculation of correction factors; Some applications of the method in mineralogy.
Introduction; Historical background of geothermometry; Origin of inclusions; Terms and terminology on fluid inclusions; Properties and characteristics of fluid inclusions. Types of inclusions; Instruments and methods of inclusion studies; Inclusion measurements and interpretation of measurements; Application of inclusion studies in various geologic environments; Future of inclusion studies.
Geol 641PT RESEARCH OUTCOMES AND SEMINAR
Geol 642PT THESIS AND VIVA VOCE
Teaching Aids & Labs
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Books